Ecommerce merchants aim to make their products competitive and the number one choice for consumers. This requires balancing many factors that affect the pricing of the product. The price needs to be affordable for customers but still bring in a profit for the business.
In this article, learn how markup percentage contributes to that goal and how to calculate it.
What Is Markup Percentage?
Markup percentage is the difference between the selling price of a product and its original cost expressed in percentages. Unit costs include expenses related to manufacturing.

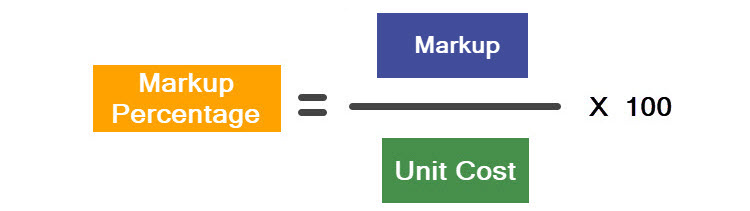
To calculate the markup percentage, the markup is divided by the cost of a unit and multiplied by 100.
The higher the markup percentage, the higher the revenue. However, there are many factors to consider when determining the selling price. These range from competitor pricing to market trends and the industry you are in. Ultimately, the right markup percentage ensures profitability while remaining competitive.
Markup Example
Here is an example of how markup percentage works:
A merchant sells a pair of pants for $80. The cost of producing, shipping, and promoting a single unit is $50, so the profit they make is $30. With this information, we can calculate the markup percentage as follows:
[(Selling price – unit cost) / unit cost] x 100 = markup percentage
[($80 – $50) / $50] x 100 = 60% markup
Note: There are various approaches to creating a pricing strategy. Explore two common ways in our article Tiered Pricing vs. Volume Pricing Explained.
Markup Percentage vs. Gross Profit Margin
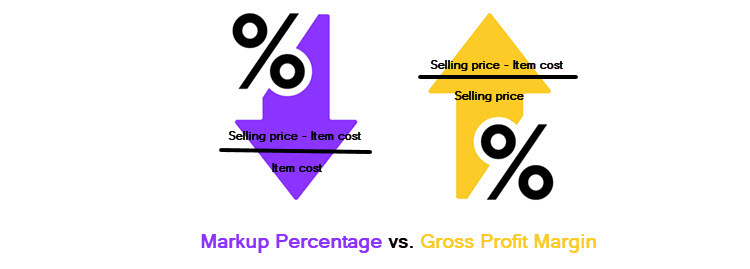
The difference between markup percentage and gross profit margin (often shortened to margin) is in how they calculate gross profit. Markup percentage expresses gross profit as a percentage of the cost, while gross profit margin expresses it as a percentage of the price.
Suppose you are selling a product that costs $20 and sells for $25. The gross profit would be $5. This dollar amount means a markup percentage of 25% and a gross profit margin of 20%. The difference in these figures is because in the case of markup, gross profit is divided by the cost while in the case of margin it is divided by the selling price.
Note: Read in detail how markup compares to margin, their definitions and how to calculate them.
Why Is Markup Percentage Important?
Markup percentage shows that you are offsetting production costs and making sure you are not incurring losses just by placing a product on the market. Markup is a percentage, rather than a flat dollar amount. It ensures that you are making a profit and covering production costs.
Markup percentage can also be used to create a pricing strategy called markup pricing (or cost-based pricing). The advantage of this method is that it is simple and quick to implement: all products get the same markup percentage added to them. Markup pricing benefits companies selling a lot products that would take a long time to individually price and items whose production costs frequently change.
However, relying on markup to determine the profitability of a company is not recommended. Markup can overestimate profits as it does not take into account the indirect costs of selling a product, such as overhead, advertising, administration, etc. For that reason, also closely watch your gross profit margins.
What Is a Typical Markup Percentage?
Markup percentages vary depending on the industry and business model. Below you will find typical markup percentages for different industries:
- Clothing. Depending on the brand, the clothing industry markup is between 150% and 250%.
- Jewelry. The jewelry industry applies a 50% markup.
- Restaurants. The restaurant industry adds up to 60% markup for food and up to 500% for beverages.
- Groceries. Grocery stores usually apply a markup of 15%.
- Automobiles. The automotive industry typically has a low markup of 5-10%. This does not include sports cars, which can have over 30% in markup.
- Manufacturing. Depending on the product, the manufacturing industry applies a markup of around 15-20%.
- Distribution. Distribution applies a markup range between 20% and 40%.
- Prescription drugs. The pharmaceutical industry adds between 200% and 3.000% markup, depending on the medication.
- Bottled water. Typically, a manufacturer spends around 5 cents to produce a single bottle of water that costs $2. This brings the markup to 4000%.
- Eyewear frames. Frames for prescription glasses have a markup range between 250% and 1.000%.
- Coffee to go. Coffee costs around 50 cents to make at home. This means that your favorite barista-brewed coffee comes with a 300% markup.
- Furniture. The furniture industry markup is between 200% and 400%.
- Cosmetics. The average retail markup for cosmetic products is 50-60%.
- Apple iPhones. Your iPhone typically comes with a markup between 40% and 65%.
Conclusion
Depending on the industry, markup percentages vary greatly so finding the right markup for your products requires market research and knowledge of production costs. Establishing your markup percentage can reduce the time and money spent on creating a complex pricing strategy. The final goal of markup is to prevent loss on the merchant’s side, at the same time ensuring the prices do not alienate customers. Understanding what is markup percentage and how to calculate it can help you improve your ecommerce strategy and increase ecommerce sales and profits.