Introduction
Magento 2 uses MySQL (or MariaDB) to store data and streamline background processes. Configuring the MySQL database parameters is mandatory when installing Magento 2 in Linux.
If the MySQL user credentials or database server settings change, the parameters in the Magento database config file need to reflect those changes.
Learn where to find and how to edit the database config file in Magento 2.
Why Edit Magento Database Config File?
The database config file contains information Magento needs to connect and interact with the MySQL database.
You need to edit the settings in the config file if:
- The database hostname changed.
- The database password or username was modified.
- You plan to use a different database for the Magento store.
Note: Learn everything you need to know about Magento database types.
How To Find and Edit Magento Database Config File?
The database connection settings in Magento are in the env.php file. The full path to the env.php file in Magento 2 is:
/Magento_Installation_Directory/app/etc/env.phpThis file also contains settings for the Magento admin URL, cron jobs, encryption key, etc.

To edit the Magento database config settings:
1. Establish an SSH connection with the Magento server.
2. Use the command-line interface (CLI) to access the /app/etc/ sub-directory in the Magento root:
cd /var/www/html/magento2.4/app/etcIn this example, Magento is installed in the /var/www/html/magento2.4 directory. Adjust the command to match the Magento root directory path on your system.
3. Open the env.php file in a text editor, such as nano:
sudo nano env.php
4. Locate the db section in the env.php file and make the necessary edits.
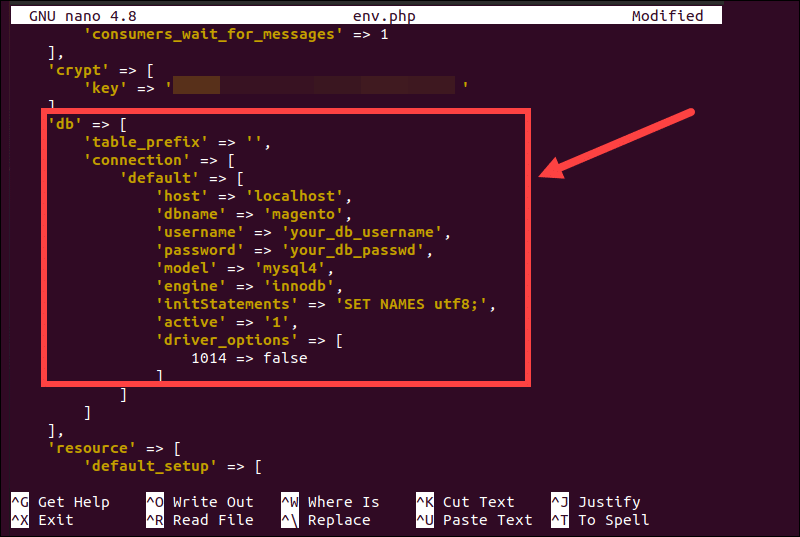
5. Edit the following parameters:
| PARAMETER | VALUE |
|---|---|
host | Enter the hostname of the database server. If Magento is on the same server as the database, use localhost. |
dbname | The name of the Magento MySQL database. |
username | Enter the username of the MySQL database user. |
password | The password for the MySQL database user. |
6. Save the changes and exit the env.php file.
Conclusion
You have successfully edited the Magento database config file. Be prepared to adjust the database settings in Magento regularly.
Ecommerce stores need to scale their servers and databases often to maintain optimal website performance. Any change to the store's underlying infrastructure can prevent Magento from interacting with the MySQL server.
