Introduction
Traditional ecommerce platforms are the driving force behind the dynamic expansion of online commerce. They provide advanced technical solutions and know-how to merchants at a fraction of their cost.
However, customer habits and expectations are changing. Paying on the go using phones, watches, and other smart devices exposes the limitations of the conventional ecommerce model.
Headless commerce is an attempt to overcome these constraints using a flexible framework. Merchants can still rely on third-party platforms to host and manage expensive backend processes but have the freedom to implement unique frontend solutions.
Learn more about headless commerce and the exciting opportunities it provides.

Headless Commerce Definition
The headless commerce model decouples the frontend of an ecommerce store from its backend application layer.
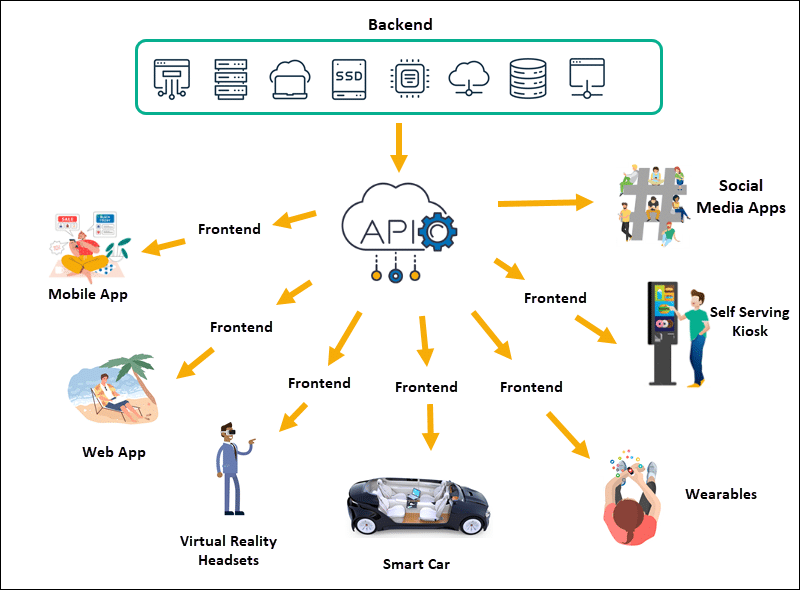
Backend applications include databases, customer management systems (CMS), inventory management, security layers, payment authentication, etc. At the same time, the presentation layer (frontend) controls how content appears on different devices.
As a result of their separation:
- The store can use the same backend applications to deliver custom content designed for specific devices and platforms.
- Marketers are no longer restricted by the architecture of the underlying platform and can freely modify the store’s presentation layer.
- Developers can work on core systems without affecting customer-facing services.
The store’s backend and frontend use APIs to communicate, maintain functionality and data consistency. REST APIs (Application Programming Interface) facilitate the secure and uninterrupted transmission of data and are an essential component of headless commerce.
Traditional Ecommerce Vs. Headless Ecommerce
An established ecommerce platform, like WooCommerce or Magento, has a user-friendly interface, professionally designed templates, and provides all the functionality and tools to run a profitable ecommerce store. Merchants do not need advanced technical skills or dedicated staff to compete successfully in a crowded market.
Traditional ecommerce models are exceptionally well-suited for web-based ecommerce. However, it is difficult to achieve a consistent customer experience across multiple devices and sales channels. Redesigning the conjoined frontend and backend applications is often costly and time-consuming.
Headless ecommerce based on APIs introduces valuable benefits to store owners:
- A Unique Customer Experience. Headless ecommerce, with its API-driven approach, allows merchants to deliver one-of-a-kind customer experiences and tailor content to specific devices or locations.
- Easy Frontend Updates. New frontend solutions are easy to implement and test as developers do not need to adjust backend services.
Building and maintaining a custom headless infrastructure requires a substantial initial investment. A headless model is ideal for a store that:
- Has a unique business model.
- Has technical staff.
- Plans to sell goods and services through several sales channels.
Merchants with limited resources can use third-party headless services to reduce the associated costs. These hybrid solutions are less flexible than a fully custom headless model but provide significant benefits compared to monolithic platforms.
Headless Commerce Use Cases
The headless commerce approach is invaluable for business models that need to reach customers regardless of where they are and what device they are using. Common headless commerce use cases include:
- Building a Custom Solution - An API-based architecture allows companies with ample resources to build truly innovative solutions. It removes the constraints of traditional platforms and allows staff to experiment and work out new ways of using existing technologies.
- Omnichannel Presence - Headless commerce is the only effective way to provide a unified customer experience on multiple sales touchpoints. Businesses can use the headless model to reach their customers systematically and on a more personalized level than before.
- Scaling - Stores that often need to redeploy their platform to accommodate seasonal or sudden increases/decreases in demand.
- Third-Party Integration - Business models that need to keep a significant level of autonomy when designing in-house solutions but cannot afford expensive backend systems. Simple API calls enable merchants to take advantage of existing ecommerce platforms, payment processors, and CMS solutions.
Large companies that adopted headless commerce have seen significant market gains. Their experiences and how they leverage the headless model can encourage smaller merchants to apply similar strategies.
Headless Commerce Examples
Brands that specialize in fashion, skincare, gaming, and fast-food restaurants were quick to implement headless commerce. Customers expect direct engagement with their favorite brands and put particular emphasis on social discovery and omnichannel payment solutions. Some of the biggest brands that recognized the advantages of an API driven approach include:
Lancôme
Convincing a new customer to buy a luxury perfume they had not had a chance to smell is tricky. But Lancôme has managed to leverage the headless commerce approach to create an immersive omnichannel experience. For example, why not virtually try on lipstick before buying it.
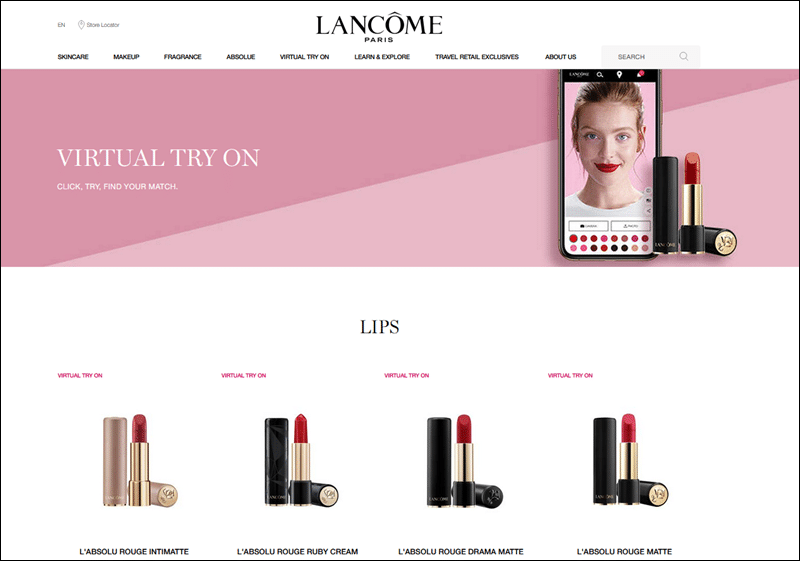
Letting customers experience products through virtual pop-up stores, online consultations, live streams, and progressive web apps has solidified Lancôme’s position as one of the most valuable global brands.
Amazon
It is not surprising that a retail giant like Amazon was among the first to recognize the advantages of a headless approach. The size of its platform would make it challenging to create and manage a monolithic solution.
Amazon uses a headless approach but at the same time proactively creates new touchpoints. The physical products Amazon produces, such as virtual assistants or e-readers, are designed to generate new sales from that device.
Amazon has become a global marketplace and arguably the most innovative force in online retail. This would not have been possible without adopting a headless approach.
Under Armor
Selling clothing and sports accessories online is a highly competitive market. Under Armor decided to apply a headless approach to speed up the customer’s journey and allow them to navigate product pages and categories seamlessly.
Under Armor continually adjusts app performance, improves speed, and clears bottlenecks based on customer shopping patterns. They can accomplish this because the headless development process is fast, lean, and lightweight.
Benefits of Headless Commerce
Customers want a personalized shopping experience on any device and in any location. The headless commerce model helps merchants respond to these demands faster and more efficiently than with a traditional platform.
- Headless commerce provides a consistent customer experience across multiple sales touchpoints.
- Teams of developers can work independently and deliver new products and services with improved speed to market.
- It is straightforward to create new tools or integrate existing solutions using API calls.
- Content creators can devise unique and personalized experiences for customers. New content does not disrupt backend systems.
- There is no need to update or redevelop the entire platform to keep up with new trends and technologies.
- Separating functionalities into microservices can improve security, website speed, and rapidly scale services with little investment.
- Testing and troubleshooting do not affect the customer experience.
The flexibility of a headless approach makes it easier for merchants to experiment and create the best possible platform.
Disadvantages of Headless Commerce
Headless commerce has several disadvantages that make it difficult for smaller and mid-sized merchants to complete the transition.
- Creating a custom headless platform is expensive.
- Finding and hiring experienced developers, designers, and content creators is difficult.
- Maintaining and continuously improving an API-driven solution requires lots of resources.
- Marketers are heavily reliant on other departments when deploying new content.
- Merchants need a large technology stack to facilitate the code bases and programming languages the different devices use.
- Maintaining data consistency throughout multiple distributed systems.
Headless commerce platforms have been developing solutions that can help merchants address some of these issues more efficiently.
What Are the Well-Known Headless Commerce Platforms?
Headless commerce platforms provide ready-made backend solutions for a distributed architecture. Merchants can use APIs to integrate their frontend with these existing background applications.
Popular ecommerce platforms include:
- Elastic Path
- Fabric
- commercetools
- Core dna
Large ecommerce platforms also offer the option to use their existing systems via an API. Some of the best know platforms include:
- Magento Commerce
- Shopify Plus
- BigCommerce
- Salesforce Commerce Cloud
Headless platforms are designed with flexibility in mind. They provide valuable third-party tools and allow merchants to create a highly customized storefront. For example, headless platforms make it easy to integrate with a payment processing API.
Conclusion
Learning how headless commerce works is an essential step before implementing the headless model for your store.
As more and more devices become connected, they become potential sale touchpoints. Headless commerce can help you reach your customers more profoundly and comprehensively than ever before.
