
How Does Payment Processing Work?
Note: PCI compliance includes adhering to operational and technical standards to protect and secure credit card information that card holders submit for credit card payments.
Payment Gateway
A payment gateway encrypts and transmits the buyer’s credit card information to the payment processor. It is a digital passage that enables online communication between the issuing bank and the acquiring bank.
Note: Read our article to better undestand the differences between a payment gateway and a payment processor.
Card Associations
Card associations are financial associations, including MasterCard, American Express, Discover, and Visa. Card associations establish qualification guidelines, interchange rates, and transaction terms for all participants in payment processing.
They are mediators between issuing banks and merchant's banks in case of any disputes.
The Stages of Payment Processing
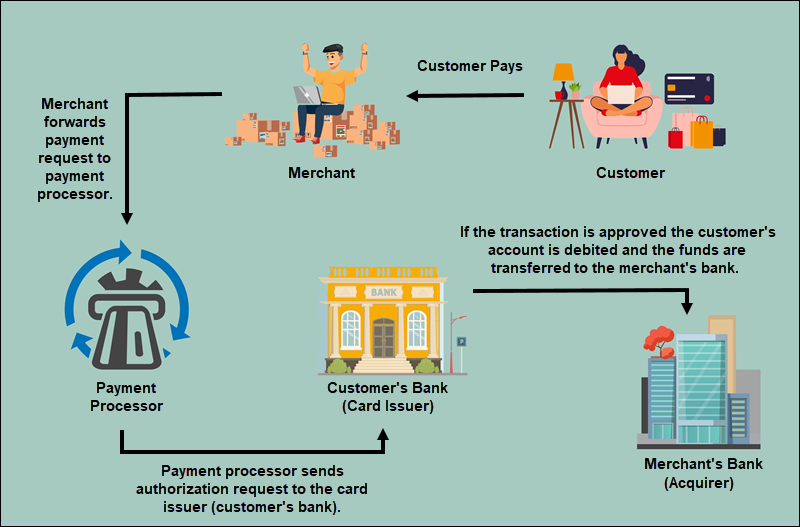
Payment processing companies implement several stages of payment processing in accordance with strict regulation. Not only do the payment processing stages below guarantee a high level of security during the transaction, but they also ensure that the payment is processed in a timely manner.
Note: Learn how long a credit card payment takes to process.
Authorization
Authorization verifies that every party in a payment processing procedure is entitled to participate in it.
It consists of the following stages:
- The cardholder provides the credit card number to a merchant to pay for purchased goods or services. Online payment requests are carried out via a payment gateway. On the other hand, brick-and-mortar stores use point-of-sale (POS) terminals to accept such payment requests.
- The merchant forwards the payment request to get authorization from their arranged payment processor. If the buyer pays for goods or services through a digital wallet, such as Google Pay, Apple Pay, or any other similar payment method, the merchant submits the transaction information to the wallet operator. The data is then forwarded to the payment processor.
- The payment processor delivers the transaction request to the relevant card association, with the issuing bank as the endpoint.
- The issuing bank receives the authorization request containing the elements of the credit card used in the transaction, such as the card verification value (CVV), the expiration date, and the address verification services (AVS).
- The issuing bank either rejects or confirms the transfer. The transaction may be declined for the following reasons: insufficient funds on the credit card, payment date has passed, or the cardholder’s account is invalid or has expired.
- The approval or denial notification is sent by the issuing bank to the card association, the merchant bank, and, eventually, the merchant.
Thanks to advanced payment technologies, authorization is usually completed within several seconds or minutes.
Note: Canceled transactions are a common occurrence in the world of merchants. Learn everything you need to know about void payments i.e. void transactions.
Settlement and Funding

Settlement is the final stage of payment processing, during which the merchant receives the amount of money that the customer paid for the purchased goods or services. Payment processing participants handle settlement and funding in the following way:
- The merchant sends a batch of authorized payments to the payment processor.
- The payment processor forwards the transaction data to the card association.
- The card association notifies the relevant issuing bank within their network of the requested debit.
- The issuing bank debits the cardholder’s account with the requested amount for the payment.
- The requested funds are then transferred to the merchant bank by the issuing bank. Interchange fees are paid at this stage.
- The merchant bank credits the merchant account with the funds in question.
Credit Card Interchange
Credit card interchange refers to the settlement and clearing of payment data, in which the acquiring bank completes the approved card payments for its merchant. This term refers to costs and fees paid by the acquiring bank to the issuing bank for the performed transaction, as well.
Note: Learn everything you need to know about credit card processing fees for merchants.
Conclusion
Merchants need to consider all payment elements and participants to ensure fast and secure payment processing. By understanding how payment processing works, merchants are less likely to face unwanted chargebacks.


