Introduction
Establishing a lasting partnership with the right payment processor helps you achieve business objectives faster and opens new avenues for future growth.
Do not waste valuable development hours on a lengthy integration. Make sure that a payment processing solution offers key services relevant to your business model.
Note: Learn everything you need to know about payment processors in our guide What Is a Payment Processor?
Find out how to choose a payment processor and use its resources to maximize revenue.
Use the following guidelines to assess the payment processor’s capabilities and check if they meet your processing requirements.
1. Pricing and Fees
Try to avoid excessive initial investment and fixed fees. The transaction fees need to be transparent and easy to audit.
A new business should look to processors that offer percentage-based and tiered pricing conditional on sales volumes.
This pricing model gives payment processors an incentive to support and work with merchants to grow their business.
2. Business Model
Payment processors often specialize in certain types of business models like subscription processing, tangible items, or token-based websites. Be sure to identify the leading payment processor for your business model and double-check if there are any restrictions on goods and services you plan to sell.
Ideally, a payment processor should offer out-of-the-box solutions that support multiple business models. Being able to introduce and scale new services quickly is a significant competitive advantage.
3. Payment Types and Currencies
Customers prefer to use payment methods they recognize and are accustomed to. A single payment form needs to offer as many payment options as possible.
Forcing customers to switch from ACH payments to credit card payments, for example, might result in them abandoning the payment form.
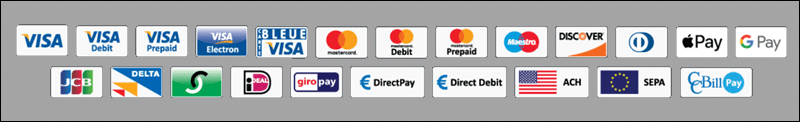
For a better customer experience, the payment processor needs to support all major currencies (USD, EUR, JPY, etc.) with automated systems that handle conversion rates.
Payment types are often restricted based on location. Always confirm what payment options are available for your merchant account.
4. Additional Features
Features and services should heavily influence the choice of payment processor. Some of the priority features include:
- A user-friendly reporting system that provides customer and sales statistics.
- Advanced API solutions.
- Flexible and customizable payment forms with the option to add cross-sells, upsells, and promotional banners.
- A well-developed referral and affiliate program.
- Streamlined integration with other third-party software (Google Analytics, eCommerce platforms, tax and ecommerce accounting tools, CRMs, etc.).
- 24/7 technical support.
Try to utilize and implement as many features the payment processor has to offer as they are designed to increase sales.
5. PCI Compliance
The Payment Card Industry (PCI) data security standards compel payment processors to fulfill a set of strict regulations. These guidelines guarantee the safety of sensitive cardholder information.
If a payment processor is not compliant with PCI standards, they cannot process credit card transactions. As a result, the merchant may only accept non-credit card payments.
Note: To learn more, check out our detailed PCI compliance checklist.
6. Global Reach
Working with a payment processor with a global presence and international experience allows merchants to reach more customers.
Even if a merchant initially plans to sell products and services locally, expanding the customer base to other countries and regions using the same payment processor is a clear benefit.
7. Earnings and Payout Methods
One of the biggest obstacles for online businesses are cash flow fluctuations. Check how often and what method the payment processor uses to pay out their merchants.
The locations of the payment processor’s bank and the merchant’s recipient bank must be taken into account before selecting a payment processor. Fees for international bank transfers can increase operating costs substantially.
8. Use Multiple Payment Processors
Even the most reliable payment processors suffer from temporary service unavailability. To avoid loss of income, use several payment processors.
Typically, customers are redirected to an alternate processor’s payment form if the primary processor runs into technical issues.
Setting up a cascade of payment forms using a second or third processor guarantees that customers can always complete their payments.
Conclusion
You can now quickly assess and choose a payment processor with enough expertise and resources to support your business. Especially if you are moving your retail shop to the ecommerce avenue and you are not familiar with how online payment processing works.
Making the right choice is going to help you automate business processes, reduce overhead costs, and increase the security of online transactions.
