In ecommerce, just like in any other industry, it’s impossible to accurately handle your finances if you don’t keep your financial records in order.
This is where ecommerce accounting comes into play. Keeping your payables and receivables under control, together with other payments, is a major prerequisite for a steady and well-planned growth in ecommerce.
In this article, you will learn everything you need to know about ecommerce accounting in the US and how it benefits ecommerce businesses.
What is Ecommerce Accounting?
Ecommerce accounting refers to collecting, analyzing, organizing, and reporting financial data related to business transactions and assets within an ecommerce business.
All the financial information that ecommerce entrepreneurs obtain via these procedures are valuable foundations for making future business decisions.
Accounting consists of three key categories:
- Bookkeeping (noting down business transactions).
- Reporting.
- Submitting tax returns.
Note: Learn everything you need to know about starting an ecommerce business.
Things You Need Before Starting with Ecommerce Accounting
The following prerequisites are necessary for carrying out effective ecommerce accounting:
- Bank account.
- Business tax ID number.
- Accounting solution.

Ecommerce Bank Account
The first stop on your road to accurate and systematic ecommerce accounting is a dedicated business bank account. Different banks offer different packages for business owners. Their offers and maintenance fees may differ, as well. Therefore, shop around several banks before you choose the right bank for your ecommerce effort.
In addition to that, it’s important to find a reliable and expedient payment processor to effectively collect online payments.
A separate ecommerce account will help you keep your personal and business assets apart, as well.
Business Tax ID Number
In the US, e-store owners need to contact the IRS to get an Employer Identification Number (EIN). This is a 9-digit number that you’re going to use on all taxation documents for your business. You don’t have to go to the IRS in person, but you can request it via an electronic form. It’s delivered to business owners via email.
It’s good to know that partnerships and corporations need to possess an EIN.
On the other hand, sole proprietors use their Social Security Number (SSN) on their tax documents and other business papers.
Note: Learn also about Tax Identification Number (TIN) in our article TIN vs. EIN: What Is the Difference?.
Accounting Solutions
Today, nobody deals with ecommerce accounting without a proper accounting solution. It’s faster, more accurate, and more convenient to manage your finances via such a tool.
Check out the key benefits of the following five accounting software options for your ecommerce accounting needs:
- Xero - Easily accessible cloud-based tool, user-friendly elements, simply integrated with other tools, automated bank processes, currency conversion.
- QuickBooks - Simple invoicing, tracking bills and costs, straightforward reporting, easy tax reporting, time tracking, and payroll.
- ZipBooks - Effective cost management, smooth credit card processing, accrual and cash reports, unlimited number of customers and vendors.
- Sage - Cash flow management, inventory and job management, customer support center, user-friendly features, scalability.
- FreshBooks - Integrated payment options, affordability, simple project tracking, enhanced invoicing.
Understanding Business Account Types

There are different types of bank accounts for businesses, depending on the number of features and their purpose. Here are the four most appropriate business account types for ecommerce business owners.
Checking Account
If you opt for a checking account, you can count on the following benefits:
- Seamless access to your deposited money.
- No request for minimum account balances. Make sure you have enough money on the account to cover your purchases.
- Usually low interest rates.
The main drawback:
- A potential limit on the number of cash deposits per month.
Savings Account
Far-sighted and responsible ecommerce entrepreneurs always put some money aside for savings. For that purpose, you need to open a savings account, knowing the following things:
- You earn interest rates on the deposited money.
- Interest rates are considered as income, so they’re subject to taxes.
- There are restrictions on withdrawing money from a savings account.
- There’s a special requirement for a minimum daily balance.
Certificate of Deposits
A certificate of deposits is a savings account to which you deposit your money for a fixed amount of time, be it one month or five years.
The key benefit:
- Interest rates are usually higher for certificates of deposits.
The major drawback:
- The money needs to be held on the account until the arranged date, otherwise penalties may be applied.
Money Market Account
A money market account combines the features of savings and checking accounts.
The main benefits:
- Higher interest rates than both checking and savings accounts.
- Suitable for ecommerce entrepreneurs with larger amounts on their accounts who want to score higher interest rates.
The key disadvantage:
- Up to six withdrawals per month allowed.
Types of Financial Statements

E-store owners must keep all their transactions and financial statements on the radar. Only when you have a clear view of your business costs will you be able to make reasonable financial decisions. By monitoring and auditing your financial reports, you can predict potential losses and avoid some risks along the way.
Ecommerce business owners need to pay attention to the three following financial statements:
- Income statements.
- Balance Sheets.
- Cash flow statements.
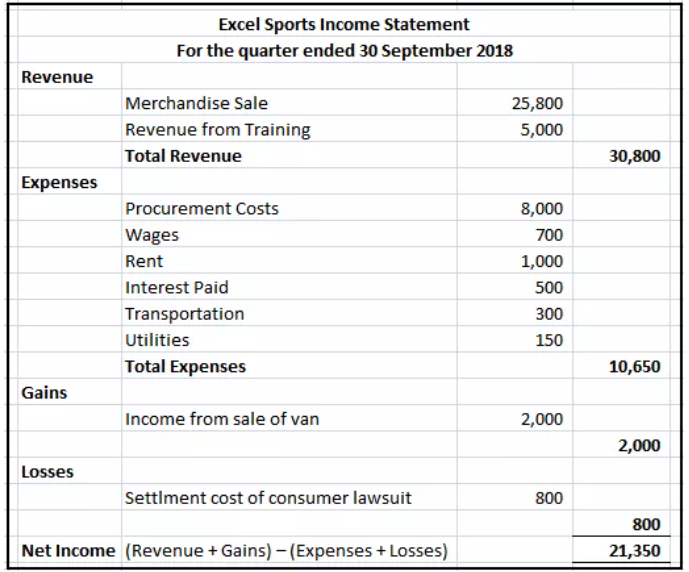
Income Statements
An income statement is a financial statement that reports business income over a specified time. Also called a profit and loss statement or the statement of revenue and expense, it covers company’s gains, losses, revenue, and costs.
Net Income = (Total Revenue + Gains) – (Total Expenses + Losses)
Below is an example of an income statement:
Balance Sheets
A balance sheet is a comprehensive report about the company’s liabilities, assets, and shareholders’ equities at a particular moment. It contains data on the possessions and debts of a company, as well as investments made by investors and shareholders.
Typically consisting of two columns, with assets on the left side, and liabilities with the shareholder’s equity on the other side, a balance sheet is based on the equation below:
Assets = Liabilities + Shareholders equity
Cash Flow Statements
A cash flow statement summarizes the cash and its equivalents being paid to and by your business. It measures the amount of cash that a company can generate to cover its debts and finance its operating activities.
The major benefits of cash flow statements:
- Informing the business owner on how company’s financial activities are managed.
- Understanding who pays the money to the company.
- Learning how the money is spent in the company.
Ecommerce Accounting Tasks
Every ecommerce business owner needs to handle various ecommerce accounting tasks on a regular level. It comes down to the following five operations:
- Categorize expenses and transactions.
- Track expenses.
- Track inventory cash flow.
- Track inventory.
- Track customer returns and chargebacks.
- Calculate break even sales.
- Stay on top of taxes.
Categorize Expenses and Transactions
Operating activities reflect how much cash is generated from a company's products and uses of cash from business activities.
The two main categories of transactions are incomes and expenses.
Modern accounting solutions automatically sort transactions on user’s behalf. Still, you should double-check every transaction and add additional categories if necessary (e.g., marketing expenditure, salaries, etc.).
This data helps you calculate monthly revenues, together with single and regular costs.
Track Expenses

In-depth ecommerce accounting includes tracking the following business expenses:
- Proof of payments.
- Receipts.
- Bills.
- Invoices.
- Financial statements from the bookkeeper.
- Previous tax returns.
- W2 and 1099 forms.
- Canceled checks.
- Various documents supporting deductions, income, or additional credit reported on your tax return.
Track Inventory Cash Flow
It’s important for ecommerce business owners to supervise and control their inventory cash flow.
An inventory cash flow report informs how much the business inventory was paid, as well as the expenses of manufacturing products, for ecommerce entrepreneurs that produce the items they sell.
Ecommerce business owners that manufacture all the products they sell need to include the following elements in the inventory cash flow:
- Raw materials.
- Maintenance.
- Acquisition of equipment.
If you want to get the full picture of the inventory cash flow and accurately calculate your net profit, it’s necessary to track inventory losses, such as:
- Spoilage.
- Theft.
- Damage during production.
Track Inventory
In addition to the inventory cash flow, e-store owners need to know the exact number of inventory items they have at their disposal all the time.
There are two ways to track inventory:
- Periodic tracking. Includes counting every single inventory item in stock and noting down the cost and sale value of each piece. Every update made in the number of inventory items is reflected in the amount of money spent and gained by your business in terms of inventory for a particular period. New e-store owners need to perform this method once a month. As your ecommerce business develops, periodic tracking is carried out quarterly or annually.
- Perpetual tracking. Rely on automated accounting software to constantly keep track of your inventory. As a new item is scanned or manually added to your inventory storage, the software tool you’re using automatically updates the inventory count and the total cash figures.
Track Customer Returns and Chargebacks
Ecommerce entrepreneurs need to keep customer returns and chargebacks separate because these are two different categories.
- Customer returns. The original transaction should be recorded as an expense and added to the accounts payable list. When the product is delivered back to your business, the customer return transaction should be listed under the Returns and Allowances section and deducted from your revenue.
- Chargebacks. A chargeback occurs when a client files a dispute in their bank in case of fraud or non-delivery of paid goods or services. All chargebacks should be filed under Returns and Allowances. In case of any extra fees due to chargebacks, they should be marked as business expenses.
Note: Learn more about the latest ecommerce fraud trends and stay on top of protecting yourself and your customers.
Calculate Break Even Sales
Ecommerce entrepreneurs need to pay attention to two types of taxes: sales taxes and business income taxes.
E-store owners based in the US have two different levels of taxes to bear in mind:
- State-level sales taxes.
- Local sales taxes.
Depending on the state where an e-store is registered, its owners need to contact the local tax administration to find out more about the ecommerce taxes they’re subject to paying.
Also, the shipping address of every single customer determines the taxes charged to that buyer. You can either enter sales taxes manually at the checkout or use a software system to automatically calculate them for you, in line with the ecommerce platform you’re using.
Note: Learn about payment reconciliation, an important process of comparing bank statements with accounting documents.
Important Ecommerce Accounting Terminology

Every ecommerce entrepreneur should get familiar with the following ecommerce accounting terms:
- Ecommerce sales tax. Imposed by the state government to be paid by retailers on sold goods and services. It’s collected at the point of sale and forwarded to the government. The formula for calculating the sales tax is:
-
Sales order. An official internal document put together by the selling party and submitted to the client to confirm and verify the sales of services and goods. It contains the following items:
- Sale details.
- Number of sold goods or services.
- Price of goods and services.
- Quality.
- Delivery address and date.
- Payment method.
- Purchase order. An official confirmation from the buyer that they wish to buy goods or services from a seller. It contains the desired quantities and pricing. Sellers make sales orders based on purchase orders.
- Invoice. A document sent by the seller to the buyer that contains the amount of money they need to pay to the seller for the arranged goods or services. While a sales order remains with the buyer, the invoice is sent to the buyer.
- Receipts. An official written document issued by the seller which confirms that the buyer has paid the seller for the arranged goods or services. Buyers use it as proof of payment.
Conclusion
Ecommerce accounting consists of numerous categories and subcategories. Online shop owners need to learn what each of these elements refer to and how to implement them in their ecommerce business.
With the definitions, tips, and instructions shared in this guide, entrepreneurs working in ecommerce have everything they need to quickly and efficiently handle their accounting obligations.
For further reading, you can check our list of free resources for ecommerce businesses in the time of Covid-19.
