According to Digital Commerce 360, online sales make up nearly 20% of total consumer spending, and this number is expected to keep growing. With that in mind, many existing businesses, as well as new retail businesses, are considering going online.
Unlike traditional brick-and-mortar retail, ecommerce consists of two key components – the physical and the digital. To expand into the online realm, entrepreneurs must register their business and set up and launch an online shop.
If you want to venture into ecommerce, learn how to start an online shop from scratch with this comprehensive, step-by-step guide.
1. Choose a Niche

Choosing a niche refers to the act of selecting a category of products to sell to a specific audience. A niche can be broad (e.g., sports equipment) or specific, also called a sub-niche or a micro-niche (e.g., tennis equipment for dry weather).
The best niche for a startup ecommerce business is a micro-niche. This is because:
- Companies have fewer competitors to worry about in micro-niche markets.
- Startups can differentiate themselves from competitors by addressing the target audience’s specific and, so far, unaddressed pain points and needs.
- An established presence in a micro-niche increases the chances of success once the company decides to expand because the audience is already familiar with the brand.
To choose a niche:
- Figure out what niche you and your employees are most familiar with.
- Look for market gaps – a target audience’s need for a particular niche product or service no competitor has developed and sold yet.
2. Choose a Business Model

Business models are established ways of doing business. It acts as a high-level business plan for building a profitable organization. Popular business models for online shops are:
- Private labeling (white labeling). The online shop sells products manufactured by a third-party, but labeled as their own.
- Dropshipping. The online shop sells products from other brands.
- Wholesaling. The online shop sells products in bulk at a discount. Usually used for business-to-business (B2B).
- Subscription services. The online shop delivers services or products to buyers on a recurring revenue model.
- Direct to consumer (D2C). Used by manufacturers to sell products directly to consumers. It effectively cuts out retailers and ecommerce platforms as the middleman.
The most popular business models for online shops, especially startups, are dropshipping and private labeling.
Dropshipping vs. Private Labeling
Dropshipping and private labeling are two business models designed for companies with little to no manufacturing and storage capacities.
Both business models outsource products, storage capacities, and fulfillment services from companies, but differ in a single thing – branding.
In dropshipping, the products being sold through an online shop are not re-branded and re-labeled. Customers receive products in their original packaging, meaning that the shop acts as an intermediary between the manufacturer and customers.

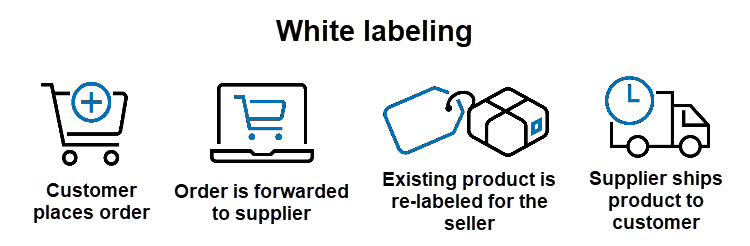
In white labeling, the products being sold are rebranded and relabeled before being shipped. This creates the illusion that the products are being manufactured by the brand on the label, which invokes a feeling of trust in customers.
If you are building a brand but don’t have the means to manufacture products yourself, opt for private labeling.
If you want to leverage the reach of multiple established brands, opt for dropshipping.
3. Choose Products
Choosing products to sell requires careful consideration of two factors - demand and logistics.
Choosing Products Based on Demand

The higher the demand, the higher the likelihood the consumer will buy a product or use a paid service. Consumers express demand for existing products or for the development of new products that would alleviate certain pain points. As a result, the best way to choose products for a new online shop is to:
- Follow trends. Accompanied by the right marketing efforts, trending products sell out quickly. Selling trending products allows ecommerce startups to get a head start on sales. The disadvantage of following trends is that they are short-lived. Keeping up with ecommerce trends requires constant market research and frequent inventory changes, both of which can be costly.
- Update and optimize a product that is popular on the market. Many products already available on the market would sell better with extra features or a design update. Optimizing existing products gives ecommerce startups an advantage even over larger competitors. Keep in mind that the optimizations must make sense. Customers do not want to pay extra for features they do not need.
- Look for market gaps. Market gaps represent the demand for solutions for unaddressed pain points. As such, market gaps allow ecommerce startups to be the first to tap into an unexplored market. The disadvantage of looking for market gaps is that the process requires extensive market research and customer feedback analysis, which is costly and time-consuming.
Choosing Products Based on Logistics
The best product for an ecommerce startup is one that does not require complicated logistics. Such products are:
- Easy to ship. Goods that are easy to ship are lightweight, compact (or sent in components), and sturdy enough to endure transport to wherever needed.
- Profitable. Products are considered profitable when they can be sold for a price that exceeds manufacturing and fulfillment costs by at least twice the amount.
- Not subject to marketing or sales restrictions and regulations. Some product categories, such as perishables or products made from certain materials, are subject to restrictions and regulations. To sell these, businesses need special licenses and permits which entail extra paperwork, product quality assurance, and fees. In addition, some marketing channels, such as social media platforms, can ban advertising for products in sensitive categories (e.g., alcohol, tobacco, prescription and over-the-counter drugs, etc.)
4. Choose a Domain
Before setting up an online shop, ecommerce business owners must decide on a domain name, check its availability, and purchase it.
A domain name refers to the web address used to visit a particular website. It represents one of the first points of contact between a prospective customer and an ecommerce business. Therefore, choosing a domain name is the most important decision an ecommerce business owner must make.
The best domain name for an online shop is one that is:
- Recognizable
- Memorable
- Unique
- Easy to read, pronounce, and type
- Easy to associate with the shop’s product offer
5. Choose a Hosting Provider
Hosting a website refers to the act of uploading and publishing a site and making it locally or globally accessible.
Ecommerce hosting can be done via:
- Web hosts. Web hosts rent storage that is used to upload websites to the world wide web. The web host is only responsible for securely storing the data someone uploads and does not participate in the design, development, or optimization of the website. This gives businesses full freedom during the design and development stage.
- All-in-one providers. All-in-one providers (more commonly known as ecommerce platforms) offer hosting services, but on top of that, they offer solutions that handle the design, development, and optimization of the ecommerce website. They also come with integrated inventory management and customer management systems, which is why they are recommended to ecommerce beginners.
The best hosting provider for an online shop depends on the needs and resources of a business but going with an ecommerce platform is always a sensible choice.
6. Choose an Ecommerce Platform

Ecommerce platforms are a type of software application that have been specifically developed for the purpose of publishing and managing an online shop. It provides all the necessary features, such as an online shop builder, inventory, customer and shipping management, etc.
Ecommerce platforms differ in many elements, such as:
- Native features
- Integration opportunities
- Scalability
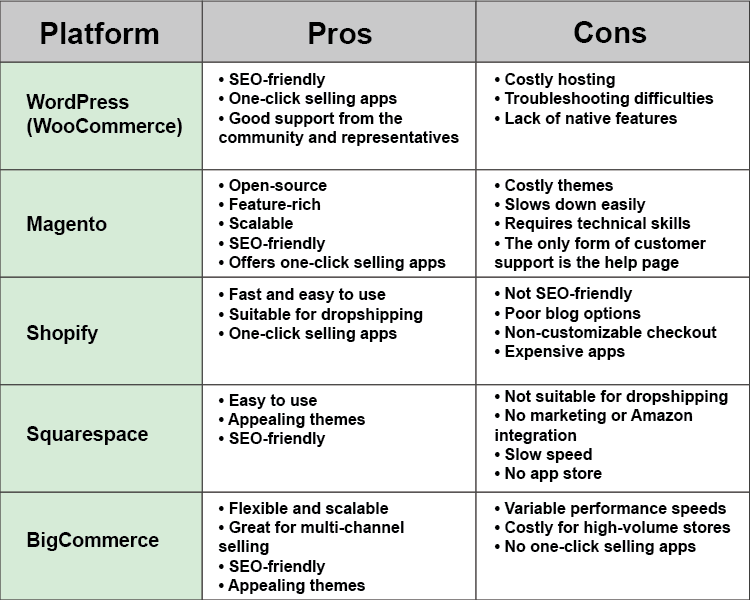
To help you choose the best ecommerce platform for your online shop, here is a brief comparison of the most popular ones.
7. Create a Visual Identity
A visual identity (also known as a brand) is a group of visual elements companies use to differentiate themselves from competitors. These visual elements can be:
- Verbal (name, slogan, tagline, term)
- Graphic (logo, design, symbol, font, color palette, imagery, physical assets, web design, advertisements)
Companies also use their visual identities to convey their visions and goals and invoke certain feelings in their audience. This is done by implementing design theory, psychology, and communication science in marketing collateral.
Determine what kind of message you want to send and the best way to achieve this. Decide whether you want to design all marketing collateral or employ a professional by outsourcing or hiring internally.
8. Set up a Business Entity

Setting up a business entity is mandatory to run an ecommerce business legally. To set up a business entity:
- Choose a name for the business. The name of the business does not have to be identical to the name of the shop. However, the name must not contain words banned in the state where you intend to register or be too similar to another business’s name.
- Select a legal structure. Legal structures are organizational frameworks that determine how many people can own a business and who is liable for any losses it incurs. An online shop can be registered as a sole proprietorship, general partnership (GP), limited partnership (LP), limited liability company (LLC), or corporation.
- Pick a location to register. Every state and country has different business regulations in place. For example, businesses in Pennsylvania do not have to file an annual but a decennial report. Nevada, Wyoming, and South Dakota do not impose corporate or individual income tax, while New Hampshire and Montana have no sales tax. Consult a legal professional to determine in which state it is best to register your business.
- Register the business. The process of registering a business varies from state to state. In most states, it refers to the act of applying for an Employer Identification Number (EIN) with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS).
- Open a merchant account. A merchant account is a business bank account used by online and brick-and-mortar merchants to accept and process electronic payments.
- Apply for additional licenses and permits. A general operating permit and EIN, which are obtained after registration, do not ensure the legality of a business. Some business activities, such as print marketing or building a warehouse, require special permits. Consult a legal professional to determine whether any additional licenses and permits are necessary to support future business activities.
Note: Learn how to open a merchant account with our comprehensive guide on the topic How to Open a Merchant Account.
When you apply for a merchant account, you will also need to undergo an underwriting procedure. For more on this subject, read our article What is Merchant Account Underwriting.
Note: Check out our article How to Start an Ecommerce Business for more detailed advice on how to set up a business entity for your online shop.
9. Choose a Payment Provider

Payment providers (also known as payment service providers, payment aggregators, merchant service providers, and third-party payment processing companies) are companies that enable businesses to accept payment card payments online.
With so many payment providers to choose from, finding the best fit for your business is a challenge. Here are key factors to consider when choosing a payment provider:
- Pricing plans. Some payment providers offer packages with a monthly fee and a fixed transaction fee, while others charge only for the transactions processed.
- Fees. In addition to the chosen pricing plan, payment providers can demand additional fees for account maintenance, statement printing and mailing, and additional services provided (e.g., payment gateway), etc.
- PCI (Payment Card Industry) Compliance. PCI compliance refers to a set of payment card industry standards every business accepting electronic payments must comply with. These standards ensure the safe collection and storage of payment information as well as secure payment processing.
- Experience with businesses in your niche. Payment providers that have experience with businesses in a specific niche understand the needs of those businesses and optimize their products and services accordingly.
- Flexibility. Payment providers should allow businesses to switch pricing plans in case of business fluctuations. Some payment providers take flexibility to the next level by creating custom plans and allowing for negotiation.
10. Choose a Payment Model

Online shops have the following payment models at their disposal:
- One-time billing. Most commonly used among online shops, one-time billing is used for non-recurring orders and represents a single charge for every individual order.
- Recurring billing. Most commonly used by subscription businesses, a recurring payment option is used when a customer orders a recurring product delivery or a Software as a Service. Recurring billing consists of a single initial charge and recurring charges, which happen when a delivery is shipped or a pre-defined period expires. Recurring billing can be upgraded with a tiered pricing model, in which merchants offer several service tiers.
- Combination. Businesses can offer both payment models, allowing customers to choose what works best for them.
The payment model you choose should be the preferred model of your target audience. It should be a model that makes sense for the type of product or service you sell.
11. Invest in Digital Marketing
A strong digital marketing campaign is crucial in establishing a market presence
Digital marketing can be divided into two segments:
- Organic (search engine optimization and content marketing)
- Paid (advertising)
Here is a closer look at some of the most popular strategies for ecommerce marketing.
SEO (Search Engine Optimization)

Search engine optimization is a free, organic marketing method that refers to the process of optimizing website content with the purpose of better ranking on search engine result pages (SERPs).
SEO for online shops involves the optimization of the homepage, product category pages, and product pages. Optimization is done by changing the code and content of your website to enhance its performance and the user experience.
These changes typically include:
- Resizing images for faster page loading.
- Minification and merging of code files for faster page loading.
- Uploading content that describes the product better (photos shot from different angles, videos, 360-degree views).
- Implementing relevant keywords in product and category descriptions.
- Organizing the content of a page in a way that matches customer behavior (what the customer expects to see first, where they want to go next, and how easy can they find what they are looking for).
According to Endpoint Digital, 35% of all ecommerce traffic comes from organic SERP results, compared to only 4% coming from SERP ads. Due of this, it is crucial to invest in search engine optimization.
Note: To learn more about the importance of SEO in ecommerce, read our article Magento SEO: A Comprehensive Guide and Checklist.
Paid Advertising

Paid advertising is a versatile marketing tool because, combined with technology and ecommerce personalization techniques, it connects customers to products they are interested in.
In digital marketing, there are six ways to use paid advertising:
- Paid search (also known as pay-per-click or PPC advertising). Brands pay ad serving companies to list their advertisements on search engines or online marketplaces. As the name indicates, the rate a brand pays equals the number of times a person clicks on an ad.
- Paid social. Brands pay social media platforms (such as Instagram, TikTok, and Facebook) to show their advertisements to target audiences.
- Native advertising. Brands or individuals pay for their content to be published on a website. This content takes the form of articles, infographics, or videos that appear as part of the website rather than as a sponsored post.
- Display advertising. Brands use Google’s Ad platform or affiliate partnerships to get their ads shown on publisher’s sites or in mobile applications.
- Newsletter sponsorships. Brands pay to have their ad incorporated in a newsletter email from a publisher, influencer, industry site or another brand.
- Podcast advertising. Brands pay podcast hosts to incorporate their audio ad in podcast episodes or talk positively about their products.
The best paid advertising methods for an online shop are paid search and paid social, so invest in pay-per-click and social media advertising.
Social Media

Social media can be used for both organic and paid marketing. Organic marketing on social media is done via relevant, relatable, and on-trend content. Paid advertising allows online shops to target their buyer persona on their preferred marketing channel.
Employ social media marketing specialists and content creators to make the most of social media marketing. Also consider whether your product would benefit from being promoted by a social media influencer.
Conclusion
You found your niche, are confident in the product, and are ready to venture into online sales. Use the information in this article as a step-by-step guide for setting an online shop from the ground up. This will ensure your ecommerce efforts bear fruit.
