Introduction
Business plans are essential for a company’s progress at any stage of development – from startups to large corporations. Ecommerce companies today face the challenge of staying up to date with ecommerce trends, offering something new to potential customers and standing out from the crowd.
Business plans are a way for a company to remain mindful of its goals, timelines, and financials. They help retailers focus on their strong suits and develop strategies that ensure growth and success. Business plans are also necessary when applying for funding from financial institutions or when attracting investors.
In this article, you will learn all about the importance of having a business plan, different business plan formats, and how to write a comprehensive and detailed plan.
Note: Learn more about how to start an ecommerce business.

What Is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a document that defines the company’s products and services, as well as its future goals. It lists the strategies, timelines, and budgets for realizing these goals.
New, smaller companies need a business plan to determine their viability, profitability, and strategies for growth. Larger, well-established businesses create and update business plans to reflect expansion, market changes, and shifting goals.
A business plan helps all levels of the company’s structure since it reminds team members of what was accomplished and what needs to be done. This includes marketing, finance, operations, and other departments within a company.
Stakeholders should review and update business plans regularly to reflect past achievements and new goals. Also, a company sometimes needs to create an entirely new business plan if it decides to move in a new direction. For example, when a company wants to target a new audience or add a different product or service to its range.
Why Do You Need a Business Plan?
There are a number of reasons why companies should have business plans.
- Strategic planning. A business plan helps companies outline and clarify the ideas behind their products and services and determine the time and resources necessary to achieve them.
- Attracting investors and securing lending. Business plans give insights into the company’s abilities and unique traits, as well as its profitability and growth potential. These are the determining factors for investors when deciding whether to support the company financially. In addition, financial institutions require business plans before granting a commercial loan.
- Researching the market. A big part of writing a business plan is researching the market and the target audience to learn its needs and how a company can fulfill them. This also includes analyzing the competition to see what they offer and, more importantly, what they lack. That way a company can focus on filling market gaps.
- Evaluating ideas. A business plan helps companies determine which ideas have more potential for success, so they can focus their time and resources accordingly.
- Staying updated with the progress. A business plan gives the company and its team members insights into the goals they need to meet. Different departments can track their achievements and honor timelines.
- Refining products and services. When writing a business plan, companies analyze how customers respond to their products and services. This helps them adjust their offering to current market trends and the needs of their target audience.
- Building partnerships. When a company approaches potential partners and collaborators, it presents its business plan to show how its goals and missions align and why the partnership would be beneficial and profitable for both sides.
- Acquiring mentorships and grants. Through business plan competitions companies at different stages of development can gain access to mentorship programs, grants, and investment capital.
- Recruiting new team members. Presenting your business plan to potential new hires is one of the best ways to get them excited about your vision and confident in your plans for the company. This is especially true for startups.
Business Plan Formats
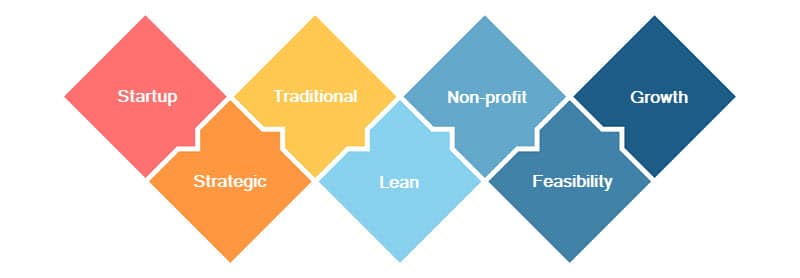
There is no standardized way to write a business plan. The goal you want to achieve is the factor that determines the format and content of the business plan.
Depending on the target audience, a business plan is internal or external. Internal plans remain for use within the company, while external plans are presented to investors, financial institutions, and potential partners.
Below we present various business plan formats.
- Startup. For startup companies, it is crucial to outline profit and cash flow projections in their business plans. This is the information that will secure funding from potential investors. This type of business plan includes sections describing the company’s background and management, plans on how it will present itself in the market, its target audience, and growth potential.
Note: If you are looking to start an online business, check out the most profitable ecommerce business ideas in 2022.
- Strategic. This business plan format details the company’s goals and mission on all levels of the organizational structure and the ways to accomplish them. It looks at the needs of the market and industry trends and outlines the concrete actions the company must take to achieve its long-term goals. A strategic business plan also includes a business’s vision and a mission statement, the description of the purpose of the company and how it sets out to achieve its aims.
- Traditional. A traditional business plan is an in-depth business plan that lists the company’s business goals. This type of business plan is the one presented to venture capitalist firms and lenders. This is the most common form of a business plan and one which takes a long time to write. It also serves as a guideline for different departments within the company.
- Lean. This is a shorter version of a traditional business plan and one that lists only key information, usually as bullet points. A lean business plan has many uses, including testing a new business idea, providing a general overview of objectives, giving a loose timeline, or onboarding new hires. It can also be used to modify an existing business plan for a specific audience or a new market.
- Non-profit. Entities that promote a public or social cause writes a non-profit business plan. It is similar to a traditional business plan and provides a description of the impact the organization intends to make in the non-profit sector. A non-profit business plan is presented to donors, new board members, and the public interested in donating or volunteering. It serves to add legitimacy to the non-profit organization.
Note: Learn how recurring donations impact non-profit organizations.
- Feasibility. Also called a feasibility study, this plan evaluates a potential new business idea to determine its potential and likelihood of success. These initiatives include offering a novel product, tapping into a new market, or targeting a new audience. A feasibility study focuses on growth potential, target demographics, and the capital needed to achieve the new idea.
- Growth. A growth business plan shows the projected growth for a new business segment. It includes the description of a new project or venture, including its market and target audience, expectations for success, capital needs and expenses. These plans are usually laid out to provide projections for each quarter, making it easier for a company to review which goals were met.
Use the table below to determine which type of business plan format to use.
| GOAL YOU WANT TO ACHIEVE | BUSINESS PLAN FORMAT |
|---|---|
| Present a new business/business idea | Startup, Growth, Feasibility |
| Detail your businesses’ goals, timeline, and budget | Traditional |
| Seek investors | Startup, Traditional, Non-profit |
| Seek a loan from a financial institution | Startup, Traditional, Non-profit |
| Test a new business idea | Lean, Feasibility |
| Provide an overview of objectives; give a loose timeline | Lean |
| Onboard new hires/board members | Lean, Non-profit |
| Detail the company’s long- or short-term strategies | Strategic |
| Attract donations and volunteers | Non-profit |
| Seek partners and vendors | Traditional |
| Find potential buyers for a business | Traditional |
| Offer a new product or service | Feasibility, Strategic, Growth |
| Enter a new market | Feasibility, Strategic, Growth |
| Update existing business plan | Lean |
How to Write a Business Plan
Here is a step-by-step guide on how to write a business plan.
1. Write an Executive Summary
An executive summary is the first and arguably the most important section of a business plan. It provides a brief overview of the company’s goals, mission, and vision. It needs to be composed so as to create interest and encourage the readers to keep on reading. An executive summary needs to be both informative and engaging.
The executive summary should not be longer than two pages. It should list the following features of your business:
- The business goal and position on the market. This is an overview of your business's short-term and long-term goals. Business goals include earning a profit while meeting your customers’ needs with your products and services, contributing to resolving social or environmental issues, etc.
- Product selection. This section states your products and services and the unique traits that differentiate them from the competition.
- The potential buyers of your products/services. Briefly describe your target audience (men/women, age, occupation if relevant).
- Communication channels for promoting products. Highlight the most relevant points of your marketing strategy, including channels, timelines, and budget.
- Current revenue. List the transparent information about your company earnings for the previous year/quarter.
- Expected profits. Give a projection of the company’s future earnings based on market research and expectations.
- Amount of money your business requires. State how much funding you need to realize your business goals and how you will spend it.
- Key members of your staff. If your team is your selling point, mention their assets briefly.
2. Describe Your Business
The second section is an introduction to your business and shows how it differs from the rest of the market. It should also show potential investors why investing in your business is smart.
A description of your business includes information about:
- Your business model and structure.
- The industry your business is in.
- Background information about your business.
- Long-term and short-term goals.
- The company values and a mission statement.
- Your staff, their skills and expertise.
Note: When determining company values, consider your ideal customer and what they want. Your mission statement addresses your customers’ needs and expectations and is the core of your business values and goals in all future ventures.
3. Present the Results of Market Research
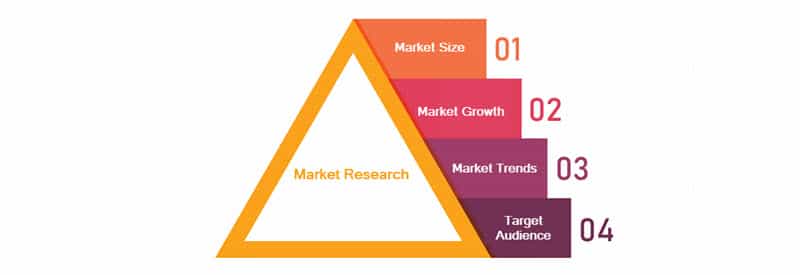
Choosing the right market for your business is crucial for success. In your business plan you will present the results of market research you performed. This section will include information about the following:
- Market size. It shows the volume and value of the market and how difficult it is to enter it and differentiate your business from the competition.
- Market growth. When analyzing market growth, focus on both previous and projected growth. Previous growth shows how the market persisted in times of hardship, while projected growth shows what you can expect in the future.
- Market trends. The market tends to move in specific directions depending on various effects, both internal (consumers’ needs and habits) and external (the current geopolitical situation, economic shifts, etc.). This forms market trends that affect the audience and the companies on the market.
- Target audience. The target audience analysis relies on its characteristics and attitude toward products and services offered on the market. It shows consumers’ habits, buying frequency and other factors that help businesses create an image of an ideal customer.
Businesses should also perform a SWOT analysis as part of their market research. SWOT stands for:
- Strengths – the things only you can do.
- Weaknesses – the parts of your business that need improving.
- Opportunities – where you can position yourself in the market to make the most of your strengths.
- Threats – market instability, changes in customer behavior/habits, your competition.
Strengths and weaknesses focus on the internal traits of your business, while opportunities and threats analyze the external factors that affect your business on the market.
4. Present the Results of Competitor Analysis

Analyzing the competition provides insight into what a business needs to do to differentiate itself from the rest of the market. A business plan contains information gleaned from this research.
The competitor analysis section includes information on the following:
- Competitive Pricing. After analyzing your competitors' prices, you can offer lower prices that will attract new audiences. The ideal price for your product will provide a return on what you spent producing it but also satisfy customer and market demand.
- Market Segmentation. Companies entering the market should first focus on conquering the competition within the smaller segments, i.e., niche markets. After that, they can easily reach more clients in larger markets.
- Market Positioning. By analyzing the competition’s offering, businesses can diversify their product range to attract a wider audience. Discover what you can do to assume a unique position in the market.
The bottom line of competitor analysis is to establish the unique value proposition of your product or service. By identifying what your competition does both well and badly, you can learn what you need to do to set yourself apart.
5. Describe the Management and Organization
This section lists the organization’s team members, their roles, and responsibilities within the company’s structure. Highlight your team’s strengths and past achievements. Also, provide information on whether new hires are required in the future.
This section also includes information on the legal status of your company, as registered with the appropriate authorities. The legal status gives information on how many people can own the company and who is liable for any potential losses.
Describing the management and organization of your company provides transparency and shows how each team member contributes to achieving the goals and the mission your business stands for.
6. Present Your Products and Services
This section details the business's products and services range, and the time, effort, and resources you put into creating them. This section should include the following information:
- A description of the goods or services you offer and what customer pain points they solve.
- The unique value proposition of your product or service.
- The production process and how much time and financial resources this requires.
- Potential plans for future product and service upgrades.
- The pricing model for your product or service.
- The supply chain the business relies on.
- The customer fulfillment strategy you employ.
Note: Learn more about different pricing models such as tiered pricing or value-based pricing.
7. Analyze Your Customer
This section creates an image of your ideal customer. It analyzes your customers’ demographics, shopping habits and interests based on the following factors:
- Age
- Education
- Residency (city or the country, with family or on their own)
- Employment
- Free time habits
- Expenses
- Beliefs and opinions.
8. Create a Marketing Plan
Creating a marketing plan defines the strategy for placing products and services on the market. Your marketing strategy rests heavily on your customer’s preferences and covers the following elements:
- The goal and purpose of your product and its price.
- The channels you will use to reach your customers.
- The resources your marketing strategy requires.
- Estimated timeline and budget.
- The metrics you will use to measure success.
Note: Ecommerce companies today rely on the omnichannel strategy to reach their customer more efficiently and track their needs and interests on the market. For more, check out our article on Omnichannel Marketing: Everything You Need to Know.
9. Write a Sales Plan
The sales plan you present in your business plan should include the following information.
In this section you can also talk about ways you intend to promote customer loyalty and ensure your customers return. If your business is based on a subscription model, provide information on how you intend to keep your customers happy and subscribed to your products or services.
Note: Customer churn and subscription cancellations are an unavoidable part of doing business. Find out what you can do about these by reading our blog articles How to Reduce Churn and 12 Subscription Cancellation Reasons and How to Avoid Them.
10. Present a Financial Analysis
Potential investors will focus on this part of your business plan as it answers questions about how much capital a business has and how much it needs to achieve goals. This is more difficult to do in the case of startups, but if your business has been around for a while, including the following documents:
- Income statement. This is a financial report that lists the company’s income and expenses.
- Balance sheet. This document lists the company’s assets, liabilities, and shareholder equity.
- Cash-flow statement. This is a statement that shows all cash inflows a company receives.
11. Give a Financial Projection
In this section of a business plan, you provide estimations of future profits. Investors look at this part to decide whether to take a chance with your business. To do this, they need to determine the following:
- When your company expects to generate profit.
- How the company intends to maintain profit.
- How you will cover your expenses and repay loans.
- What return on investment they can expect.
You need to strike a balance between optimism and caution: do not make the mistake of underestimating the obstacles you might face and the expenses running a business incurs. Be realistic in the expectations you have of your business, market fluctuations, and your investors’ readiness to take risks.
Conclusion
Writing a business plan is crucial for the development and success of any business. Business plans have many uses, from defining the company goals and mission to attracting new partners, hires, and financial support. They are an excellent way to keep track of your timelines, budgets and plans for achieving long- and short-term goals.
Companies need to write and revise their business plans regularly to keep abreast with the changes happening both inside the company and on the market. This helps them tweak their processes and goals to match current trends and add new solutions to their business flow while keeping their clients interested and returning.
