Introduction
Payment information needs to be shared and verified by multiple participants in the payment process. Safeguarding and transferring payment details is a primary concern for merchants, banks, and payment processors when dealing with online payments.
Tokenization limits the exchange of sensitive information and reduces the risk of it falling into the wrong hands. At the same time, tokens can turn online payments into a convenient and carefree activity for customers.
Find out how credit card tokenization prevents fraud and why tokens drive online sales.
What is Credit Card Tokenization in Payments?
Tokenization turns a customer's payment details, like a credit card number, into a unique randomly generated set of characters, called a token. The token can then be used to make payments without re-entering or referencing the credit card number.
A token does not have a logical connection to the data it represents. It is impossible to retrieve the primary account number (PAN) or other payment data by analyzing or decrypting a token.
A token service provider (TSP) is responsible for validating, creating, and storing tokens. The TSP maintains a highly secure token vault that pairs tokens with a customer’s PAN.
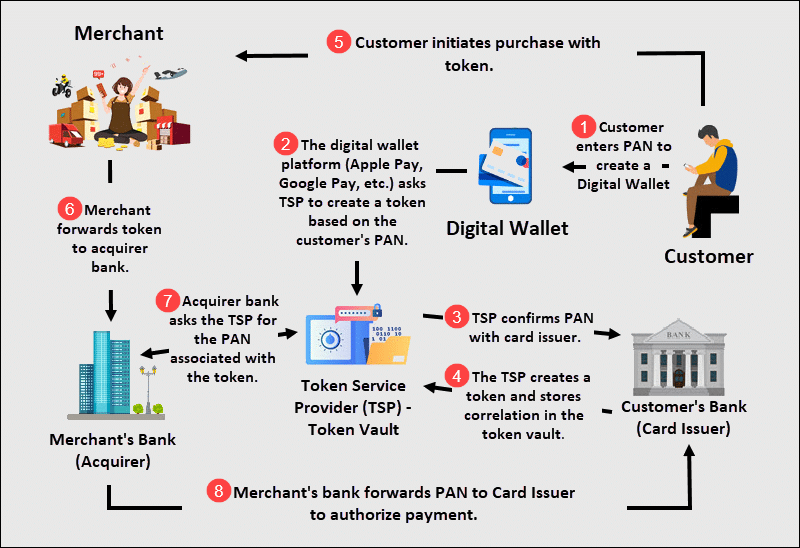
The complete validation and authentication process is conducted by the Merchant Acquirer, TSP, and Card Issuer.
The merchant no longer needs to store or exchange sensitive data with the customer. The PAN and token are safely stored in the TSP token vault.
Note: If you are a merchant looking to learn everything about credit card processing, visit our post How Long Does a Credit Card Payment Take to Process?
Benefits of Payment Tokenization
Substituting personally identifiable information with a token increases the security of transactions significantly. Tokens also provide exciting opportunities for streamlining and enhancing the customer’s shopping experience.
Some of the benefits include:
- Customers do not need to enter payment details for every purchase.
- Merchants no longer deal with sensitive payment information.
- The PCI Compliance scope for merchants is reduced.
- Well-suited for in-app and mobile transactions.
- Tokens are not susceptible to personally identifiable information fraud.
- A single PAN can be used to create an unlimited number of tokens. This means that customers can have one credit card and multiple tokens for different devices or various payment gateways.
- If a token is compromised, the customer does not need to change their credit card.
Allowing customers to pay and upgrade with a single click from multiple devices and platforms is sure to increase sales and revenue. Merchants can now shift focus from protecting payment data to developing their services and encouraging customers to spend more freely.
How is Tokenization in Payments Different from Encryption?
Encryption uses an algorithm to turn information into an unreadable set of characters. The receiving party uses a unique key to decipher the message and access the sensitive information. Encryption has long been an integral part of payment processing.
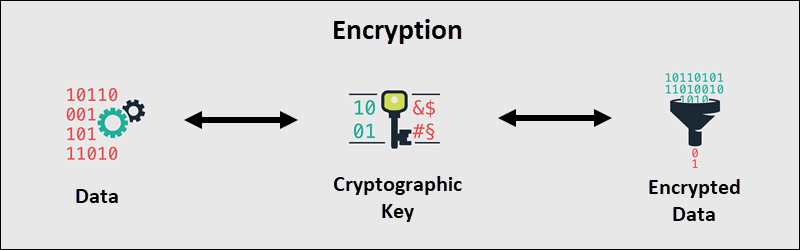
If an encrypted message is intercepted, it might be possible to reverse the encryption.
A token is merely a substitute for the actual information and does not contain relevant or valuable data. Someone who intercepts a token would not be able to extract any useful information from that token.
Tokenization and encryption are usually used together in payment processing. The data is first tokenized, and then that token is additionally encrypted. Combining these two methods significantly reduces the risk of fraud.
Note: Read more in-depth about Tokenization vs Encryption.
Credit Card Tokenization and PCI Compliance
The PCI (Payment Card Industry) data security standards guarantee that organizations dealing with cardholder information adhere to a strict set of guidelines. Not complying with PCI standards can result in a loss of reputation, paying damages, and ultimately not being able to accept credit card transactions.
Tokenization is not a requirement for PCI compliance.
Tokens help merchants reduce the amount of sensitive information they need to receive, store, and transmit. Using tokens instead of the customer’s PAN decreases the number of standards merchants need to comply with.
Tokenization can reduce PCI-related costs and make it easier for merchants to pass PCI audits successfully.
Payment Tokenization Examples
Customers primarily pay from devices they turned into digital wallets (Apple Pay, Google Pay, Alipay, CCBill Pay, etc.). E-commerce merchants also use tokens to store customer payment credentials and initiate recurring payments or make on-demand purchases easier.
It is possible to create multiple tokens using a single credit card (PAN). For example, Yoshi and Imoen share a credit card:
1. Digital Wallet - Yoshi creates a Google Pay token on his Android phone. He uses his phone to make contactless POS payments in his local store without using the credit card.
2. Wearables - Yoshi creates another Google Pay token on his smartwatch. While exercising in the gym, Yoshi buys a bottle of water using his smartwatch. He does not need to use his credit card nor his mobile phone.
3. In-app payments - Imoen creates an Apple Pay token on her iPad using the same credit card. Imoen buys upgrades within her favorite game without entering card details or exiting the app.
4. Card-on-file and recurring payments - Imoen signs up for services on SiteX using the credit card. The site requests a token from a TSP and no longer needs to store credit card details. Imoen can shop on SiteX without needing to enter card details again.
Merchants with a subscription-based payment processing model no longer need to store card details; they can charge the customer using the token. TSPs ensure that tokens are unique to each merchant.
5. IoT payments - Imoen creates a token in her Tesla? This might not be the case at present, but an increasing number of devices is always online. A token in a car, for example, would allow you to buy software solutions, hardware components, or services geared specifically for that model. Using tokens for such purchases seems like a natural fit. For now, token provisioning for IoT devices applies the same model as for other e-commerce transactions.
Coupling device-centric tokens with advanced authentication methods like biometrics is going to shape the future of online payments.
Note: Learn more about payment processing by referring to our article How Does Payment Processing Work?
Conclusion
You now understand the benefits of tokenization and why tokens are an integral part of the payment process.
The impact tokenized payments have on merchants and customers is going to create a secure environment and transform online payments into the safest and preferred payment method.
