Introduction
Card associations, payment service providers, and banks work together to protect cardholders, prevent payment disputes, and help businesses reduce liability risks.
They use merchant category codes (MCCs) to facilitate early payment fraud detection, risk management and enforce local and international regulations.
Every merchant is awarded an MCC before they can start accepting card payments.
Learn more about Merchant Category Codes and find out how they impact your payment processing fees.
What is an MMC - Merchant Category Code?
A Merchant Category Code (MCC) is a four-digit number that categorizes businesses based on the types of products and services they offer.
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) classifies business activities into hundreds of merchant categories. Each category has an associated Merchant Category Code.
Merchant Category Code examples:
| MCC | Merchant Category Description |
|---|---|
| 4186 | Computer Network/Information Services (Web Design) |
| 5967 | Direct Marketing - Inbound Telemarketing Merchants |
| 5999 | Miscellaneous and Specialty Retail Store |
| 7273 | Dating Services |
| 7299 | Miscellaneous Personal Services |
| 5815 | Digital Goods: Books, Movies (Educational), Music |
| 5499 | Miscellaneous Food Stores - Convenience Stores, Markets, Specialty Stores, and Vending Machines |
Card networks (Visa, Mastercard, Amex, Discovery, etc.) maintain their own MCC lists based on the ISO standard code values. Card brands regularly update their MCC lists by adding new codes, removing obsolete MCCs, and updating guidelines based on the latest risk assessments. They also impose processing rules and restrictions for individual merchant categories.
The merchant's bank or PSP awards the merchant an MCC according to the rules outlined by their partner card network.
How Are MCC Codes Used?
A merchant category code informs participants in the payment process about the merchant’s core business model. MCCs are important because some merchant categories are more susceptible to fraud and have higher chargeback rates.
Financial institutions, PSPs, and card networks use MCC to:
- Calculate risk levels based on the history of chargebacks, refunds, and returns in a specific merchant category.
- Develop automated solutions to monitor, detect, and restrict fraudulent credit card transactions.
- Coordinate fraud-prevention initiatives such as the Mastercard BRAM (Business Risk Assessment and Mitigation) program and Visa’s Global Brand Protection Program (GBPP).
- Assess merchants during the registration process and deny untrustworthy businesses access to processing accounts.
- Collect and analyze data about cardholder purchasing behavior.
How to Find MCC Code?
A merchant can find the MCC by contacting their payment processor. The payment processor can quickly determine which MCC is associated with the merchant's account and how that MCC affects payment processing fees.
For example, CCBill merchants can contact Merchant Support and learn their MCC within minutes.
Existing merchants can also access the Admin Portal and verify their Merchant Category.
1. Access the Admin Portal.
2. Click Account Info.
3. Select Feature Summary.
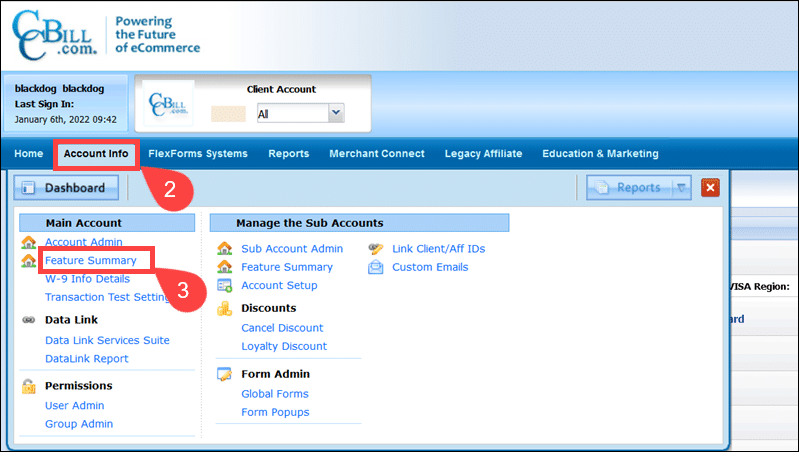
4. Locate the Merchant Category field.
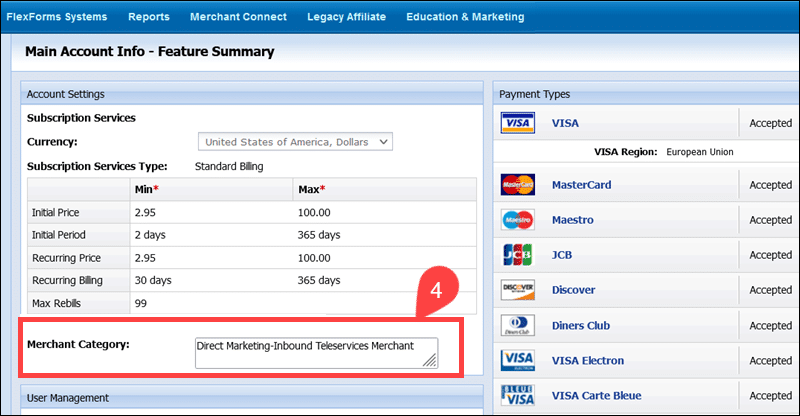
The category description shows that the merchant's main field of activity is Direct Marketing - Inbound Telemarketing Merchants.
This type of business is associated with MCC 5967, which you can discover by visiting the Visa MCC Directory or the Mastercard Quick Reference MCC Booklet.
Merchant Category Codes and Payment Processing
Typically, the merchant's PSP (or acquiring bank) evaluates the merchant's business model and registers the processing account under an appropriate MCC.
Merchants cannot choose the MCC their processing account is going to receive. Some merchant categories contend with higher levels of payment fraud so financial institutions and payment processors consider them high-risk accounts.
The difference between low-risk and high-risk accounts in terms of processing fees can be substantial.
- Businesses deemed to have high-risk business models have higher processing rates.
- Merchants with high-risk business models may need to pay additional fees in case of chargebacks, returns, and refunds.
- A certain percentage of every transfer made to a high-risk merchant account may be used as a rolling reserve.
- Merchants with a high-risk MCC may be required to pay a registration fee to become a Visa Sponsored Merchant or be a part of MasterCard's Payment Facilitator Program, depending on the type of service, product, or content they sell.
- Issuing banks and card networks restrict processing for specific high-risk MCCs to meet local regulations or prevent potential brand-damaging activity. For example, many issuing banks do not allow payments on gaming (betting) websites. An issuing bank can easily enforce these restrictions by blocking transactions for merchants that have MCC 7995.
- Merchants may encounter limitations on the number of transactions or the total amount they can process in a given period.
Many payment service providers only work with low-risk merchant processing accounts. PSPs with robust validation and authentication systems, like CCBill, process payments for both high-risk and low-risk accounts.
Note: Learn about the differences between chargebacks and refunds.
Why is a Merchant Category Code Important?
Merchant category codes are not used solely for assessing risk levels and preventing fraud. The MCC guidelines defined by payment brands have a profound impact on the entire payments industry.
- Participants in the payment process use merchant category codes to obtain comprehensive data about customer behavior. Analyzing this data can provide valuable insight into market and industry trends.
- MCCs are integral to advanced software solutions, authentication tools, and other automated systems within the payment processing ecosystem.
- Depending on local tax regulations, the MCC can determine if a merchant needs to report or pay sales or income taxes.
- Payment card companies use MCCs to build loyalty programs around their brands. They give customers incentives such as cashback or reward points for purchases in specific merchant categories.
Conclusion
Merchant category codes are a straightforward and efficient way to keep track of and control transactions on a large scale.
MCCs allow payment card brands to define and modify rules for card transactions in individual merchant categories.
If you have a high-risk business model, you need a payment processor that can guide your business through the frequent MCC rule updates.
