The emergence of new technologies and ecommerce innovations has changed how merchants form their business relationships. Omnichannel is a holistic approach to marketing that places customers at the center of a multichannel marketing effort.
Omnichannel relies on multiple mutually connected communication channels. Customers switch between these channels seamlessly, without breaking contact with the brand in question.
A relatively new concept, omnichannel elevates your customers’ buying experience to a new level.
This article explains what omnichannel is, how to implement it, and describes the benefits and challenges it brings to merchants.
What is Omnichannel?

Omnichannel is a customer engagement approach that relies on at least two or more integrated channels. This includes multiple, mutually related touchpoints, such as mobile, social media, email, website, and brick-and-mortar stores.
Omnichannel puts the customer experience in the spotlight, rather than products or the brand in question. Customers jump between various channels while staying connected with the brand throughout a shopping session or any other interaction.
Let’s say that a customer contacts a merchant via a live chatbot and this service doesn’t provide the right answer. The customer is immediately redirected to a FAQ session and a customer support agent. In this case, the customer support omnichannel experience consists of three interrelated channels.
Note: Learn more about CCBill's Omnichannel Payment Solutions and start working with CCBill today!
What Are the Differences between Omnichannel Vs. Multichannel?
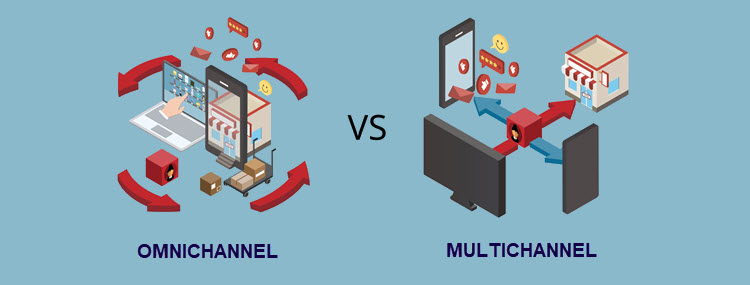
The main difference between omnichannel and multichannel is that customers can’t seamlessly switch between channels in multichannel marketing.
Multichannel focuses on enhancing the customer relationship with the brand through several independent channels. The channels usually deliver the same message but they are not synchronized or connected with one another. Customers use one channel at a time and break interaction with the brand to switch to another channel.
Omnichannel focuses on the mutual integration of various channels and continuous customer engagement. Omnichannel tools collect data on the user’s behavior and adapt the marketing messages the customers receive in real-time. An example of this in retail would be a mobile app and an ecommerce website that sync the buyer’s cart in real-time. Bear in mind that omnichannel is at the same time multichannel since it involves the use of multiple communication channels.
Note: Learn more about the differences and similarities between omnichannel and multichannel from our post Omnichannel Vs. Multichannel: What Are the Differences?
Examples of Omnichannel
As more brands turn to a holistic approach to marketing, there are more examples of omnichannel. Below are some examples that stand out.
Amazon
Amazon is one of the global pioneers of omnichannel and remains at the forefront of buyer-friendly options.
Registered and signed-in users enjoy the benefit of having their carts synced on different channels – the website, the mobile app – and various devices used for buying on Amazon.
Also, you don’t have to sign in to make a purchase on Amazon. There’s a guest checkout option, so that non-registered buyers can finish their shopping there.
Closely related to omnichannel, Amazon offers its buyers different cross-selling and upselling options. For instance, paying the Amazon Prime monthly or annual subscription provides users with more convenient delivery options and various discounts for Prime multimedia services.
Nike
Nike is another big brand that has been using omnichannel for several years. Their main goal is to integrate physical and digital services into a unified shopping experience.
What started with the Nike Plus program in 2006 has now become a membership-based omnichannel strategy that brings the best of Nike to loyal customers. Getting member-exclusive products at special prices and customized offers are only some of the many benefits that members obtain from this approach. What’s more, customers can download various apps – Discover, Run, Workout, to name a few – and sign in with their Nike account.
All these apps and tools track and collect users’ personal and shopping preferences to prepare tailor-made offers and enhance the omnichannel experience.
Pros and Cons of Omnichannel
Omnichannel has revolutionized the ecommerce industry by bringing the following benefits:
- Frictionless customer experience. Allowing customers to transition between communication, support, and marketing channels without noticing it makes for a unique and frictionless customer experience.
- Increased purchase rate. Using omnichannel increases the merchant’s overall purchase rate, when compared to using a single channel or multiple separate channels.
- Higher customer expenditure. As reported by the Harvard Business Review, omnichannel retail campaigns increase the amount of money customers spend, raising the brand’s annual revenue and ensuring a steady cash flow.
- Boosted engagement rate. When customers switch from channel to channel within the same brand without interrupting the interaction, their engagement rate with the company is much higher. They are more active, which increases their buying potential and the customer lifetime value (CLV) while reducing and preventing churn.
-
Enhanced loyalty. Merchants using omnichannel provide their customers with services across a broad spectrum of digital and analog channels. The more actively a customer uses these services, the more information the merchant gathers about them. Consequently, merchants have more input to work with, while occasional customers enjoy more potential perks and turn into recurring customers.
-
Improved customer acquisition. Omnichannel enables merchants to acquire new customers more easily, leading to more dynamic business growth.
-
Optimized operational efficiency. Merchants relying on omnichannel collect vital customer data only once and use it to provide customized offers throughout different channels. Other relevant customer information is collected along the way and used to prepare those offers. Omnichannel also opens room for implementing automatic payments and other recurring billing options which ease payment processing.
-
Better inventory tracking. Omnichannel tools help merchants get detailed information on their current inventory and avoid shortages. They also provide valuable insights that can shape their future investments on the basis of their customers’ buying habits.
The omnichannel approach also presents merchants with some challenges. These are:
-
Technical requirements. Using a variety of interlinked channels to communicate with clients, promote products and services, and provide customer support requires complex technical solutions. The front-end needs to look as simple and user-friendly as possible, and it must ensure a smooth customer experience. The back-end is usually complicated to develop.
-
Expensive. Considering developing a holistic omnichannel strategy requires complex technical solutions, it is also expensive to develop. It requires experienced software engineers by your side. For some merchants, it ends up being too expensive and time-consuming to lay down an omnichannel strategy.
- Intensive communication between teams. Teams in charge of different channels within the same omnichannel strategy need to have continuous and clear communication. Multiple teams and their members must work together to always be ready to respond to customer requests, demands, and complaints.
Note: Stay on top of everything new in omnichannel retail with our article Omnichannel Retail Trends.
How to Implement an Omnichannel Strategy
Merchants that want to implement an omnichannel strategy in their business operations need to take the following steps:
- Collect customer data and analyze it thoroughly to understand who your customers are, what they want, and how they use different channels.
- Personalize offers for your products and services based on your CRM system and modern analytical tools, using the obtained customer data.
- Invest in interactive technology, like AI chatbots, to increase customer engagement on the website, the app, and the store. Provide smooth transitions between these touchpoints.
- Come up with original in-store solutions that are easily integrated into an omnichannel strategy. The store must provide excellent UX to impress the existing customers and attract new ones.
- Take on the role of a customer and follow their journey across your omnichannel system to make sure that the transition between channels is smooth. Work together with your designers and developers on polishing up the bumps you come across along the way.
- Strengthen your social media presence and promote all touchpoints.
- Offer 24/7 omnichannel customer support that includes chatbots, live customer support agents, email service, FAQs, troubleshooting, and any other necessary elements to help your customers.
- Train your workers to react properly in the new business environment. Omnichannel often requires immediate reactions from members of different teams to resolve potential issues and ensure a pleasant customer experience.
Conclusion
Omnichannel is undoubtedly the future of ecommerce, digital marketing, and customer support. As people’s online habits and technologies change, there’s a growing need for new channels. Merchants that seize this opportunity are more likely to ensure continuous business development.
This guide will help you understand how omnichannel works and what it takes to implement this holistic approach for future business growth.