Introduction
Asking customers to voluntarily provide private and sensitive data, getting to know their preferences, and establishing a trusting relationship are at the heart of retail and ecommerce.
Sophisticated security features and tools designed to protect customer information are often expensive and unattainable for smaller merchants.
Ecommerce merchants with limited resources can reduce risk levels considerably by applying proven security practices and procedures.
Find out how to protect customer information on an ecommerce website.
How to Protect Your Customers' Privacy and Data
Ecommerce stores need customer data to authenticate secure online payments, deliver goods and services, and personalize communication.
Protecting that data vigorously is the only way to ensure the long-term success of an online store. To protect customer data:
- Reduce the attack surface and do not collect redundant data.
- Work with other participants in the payment process, like payment processors and customers, to identify and prevent fraud. Data protection is a collective effort.
- Ensure that all systems and software solutions are up to date.
- Manage privileges and give users access only to data required for their work.
- Create a damage limitation plan if a breach does occur.
Use the following 15 best practices to protect your customers and their data proactively.
1. Only Collect Essential Customer Information
Data is a valuable asset, and, understandably, merchants want to gather as much customer information as possible.
The amount of data a store collects needs to reflect its business model. For example, the customer's phone number is not essential for a website selling downloadable digital content.
Do not collect and store customer payment information. If possible, limit the collection of data to the customer's:
- Name
- Address
Keep in mind that forcing customers to divulge too much information during checkout also hurts conversion rates.
2. Use a Trusted Payment Processor
Payment processors invest heavily in data security and fraud prevention tools. Choosing the right payment processor allows ecommerce merchants to use these tools at a fraction of their cost.
Besides an impeccable security track record, the payment processor also needs to provide:
- Advanced API solutions - Merchants can use APIs to automate customer data management and reduce customer information they need to collect and store.
- 24/7 technical support -Support services that actively monitor and counteract suspicious activity are vital for preventing fraud.
- PCI Compliance - Complying with the Payment Card Industry (PCI) data security standards guarantees the safety of sensitive cardholder information.
Personally identifiable information (PII) is much more secure in the hands of a large organization like a bank or payment processor.
3. Apply a Reasonable Password Policy
Ecommerce websites use passwords because they are free, scalable, and customers understand how they work.
Passwords are the first line of defense for protecting customer information, making them a prime target for DDoS attacks, Brute Force attacks, and Account Takeover Fraud.
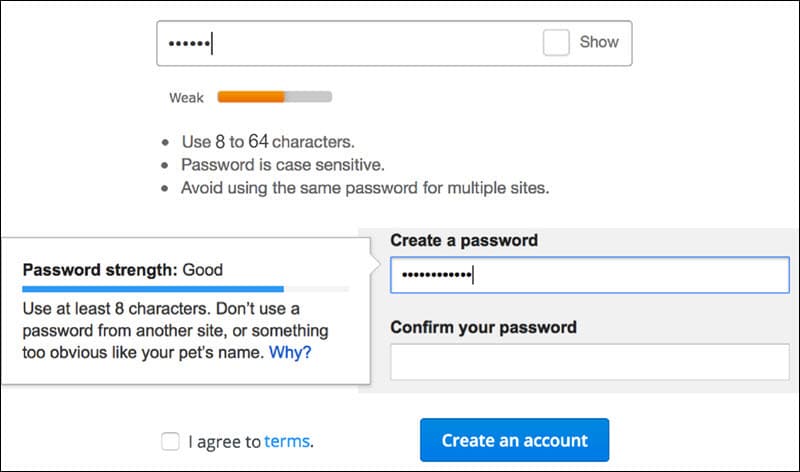
Strict policies that force customers to create complex credentials do not improve the quality of passwords. Customers frequently compromise password strength as they try to find ways to circumvents these restrictions.
Motivate customers to create strong credentials on your ecommerce website by applying password policy best practices.
4. Limit Access to Customer Information
An ecommerce store needs to precisely define employee roles and restrict access to customer information based on those roles.
Employees that use customer data for work-related tasks are the only individuals that should have access to sensitive customer information.
For example, a customer support representative needs such access, but there is little reason for a website designer to have the same privileges.
To further improve data security, implement additional features such as two-factor authentication and only allow users from whitelisted IPs to access customer data.
5. Use Two-Factor Authentication
Customers are beginning to appreciate the advantages of two-factor authentication (2FA) and systems like 3D Secure. However, merchants are concerned that implementing 2FA may disrupt the payment flow on their websites and increase abandonment rates.
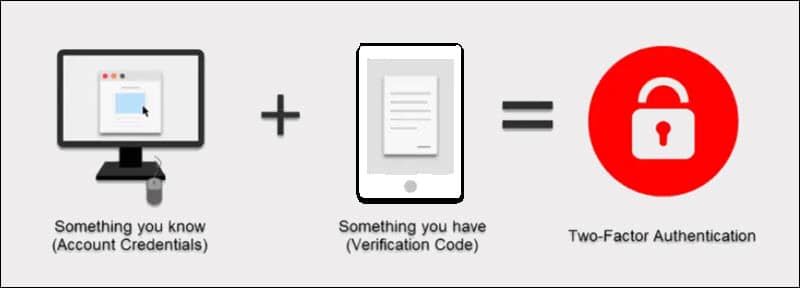
2FA is highly effective in preventing fraud. Do not allow customers to change account details or update their credentials without additionally authenticating such requests.
Use 2FA to ensure that employees always need to verify their logins when accessing sensitive customer data.
6. Implement SSL on Your Website
Implement an SSL (Secure Socket Layer) certificate to secure customer sessions while they browse the store. The certificate establishes an encrypted connection between the store's server and customer's browser and makes it much harder for attackers to intercept data.
The cost of SSL certificates depends on the number of domains and subdomains and the validation level.
Research the different types of SSL certificates and find out what kind of certificate you need.
Organization Validated and Extended Validation SSL certificates are more expensive, but the level of protection they provide is better suited for ecommerce stores.
7. Keep Software Solutions Up to Date
Attackers constantly and actively seek out systems that do not apply security patches and fixes. Some of the largest security breaches were the result of outdated software.
Review and update core systems, all custom solutions, and plugins regularly. Neglecting to implement the latest software version or security patch is a significant security flaw.
Take special care when updating custom software and plugins and test extensively to identify vulnerabilities. Ensure that cross-compatibility with other systems is maintained at all times.
8. Invest in a Secure Dedicated Server
Dedicated hosting is more expensive than shared hosting but has several clear advantages:
- Security -You no longer need to worry about security gaps caused by other server tenants. Dedicated servers provide merchants with better data recovery capabilities, enhanced DDoS protection, and efficient IP address blocking.
- Performance - Isolating and using dedicated physical resources like hard drives, CPUs, bandwidth, and memory significantly improve website performance.
- Flexibility - Implement new and custom applications, security features, and strict access control.
Dedicated servers add a new layer of protection to customer information and proprietary business data.
9. Have a Disaster Recovery Plan in Place
Natural disasters, outages, and compromised security (ransomware, malware, etc.) can lead to a complete loss of customer information.
A disaster recovery plan is a set of procedures and guidelines that outline what employees need to do in such circumstances. To minimize the effects of a disaster:
- Back up your ecommerce store and customer data at regular intervals using advanced backup and recovery systems.
- Clearly outline critical activities and staff responsible for carrying out these activities.
- Appoint a person or team responsible for communicating with customers, external partners, and employees.
- Identify and list essential tasks after the data has been recovered.
Create a detailed plan for every activity and ensure that both internal and customer-facing communication is as clear and transparent as possible.
10. Show Customers They Are Protected
Online shopping needs to be an enjoyable and carefree activity. Customers are less likely to buy products and share information on websites they deem to be insecure.
Build trust and reassure customers by showcasing what measures and steps your website takes to protect their data.
HTTPS is a good example that explicitly shows customers that the connection is secure.
Show customers that their personally identifiable information is safe from the moment they reach the website until they conclude the payment process.
11. Use a Firewall
Authentication tools are excellent for preventing unauthorized access to sensitive data. However, ecommerce websites need firewalls to verify network traffic and identify harmful content before it reaches their systems.
Different types of firewalls scan content and prevent malicious external traffic from entering internal networks. The firewall uses predefined rules and policies to determine if traffic is permitted to enter the network.
In addition, stores need to identify malicious activity within the network using intrusion prevention systems (IPS) and anti-virus software.
12. Employ Good Email Practices
Emails are the most common vehicle attackers use to infiltrate the user's systems. Phishing emails and social engineering rely on recipients clicking links, opening documents, or downloading attachments that contain malware.
To prevent breaches that target customer data, train your employees, and define strict email procedures.
- Employees must create strong email passwords and update them regularly.
- Staff should not utilize business emails for personal use.
- Do not access business emails from public Wi-Fi connections.
- Do not click links or open attachments in unsolicited emails.
Expand these policies and find ways to convey their benefits to customers as well.
13. Educate Your Customers
Many data breaches result from attacks and activity that occurred outside of an ecommerce store.
Customers are active participants in any data protection strategy, and they are often the first to notice that something is wrong.
- Provide examples of how attacks happen so that customers do not make the same mistake.
- Give data protection advice on your FAQ pages, blog, and social media channels.
- Organize activities such as quizzes about data security and give out vouchers to customers that participate.
Customers that avoid risky behavior and know how to react if they notice suspicious activity are a true asset for any ecommerce store.
14. Employee Training
Ecommerce stores need to implement strict data protection procedures and train staff that handle customer information.
Frequent workshops help employees recognize common threats and understand how their actions can assist or prevent attacks. They need to know how to react if a customer reports a breach, what action to take when an attack is underway, and how to handle the repercussions of a successful breach.
The quality of the training affects staff reaction times and makes damage control much more efficient.
Employees need to have access to relevant training courses, and the materials should reflect the latest standards in data protection.
15. Test For Vulnerabilities and Weak Points
A vulnerability test helps store owners discover security flaws in their systems before an actual breach takes place. The testing should not be limited to the store's IT systems. It is equally important to assess employee reactions to simulated attacks and adjust procedures and training courses accordingly.
Always perform limited vulnerability assessments when adding new services or hardware. Using in-house staff to test for vulnerabilities is cost-effective, but specialized third-party services are more likely to discover weak points.
Conclusion
By applying these practices, you have improved customer data protection on your ecommerce website.
Data protection is an opportunity for ecommerce merchants to demonstrate how much they value their customers. If they feel safe, customers are going to engage with website features, interact with the merchant and other customers, and form a genuine community around your store.
