Introduction
Modern APIs are reshaping the payment services landscape. Innovative concepts, like headless commerce and progressive web apps, enable merchants to reach customers anywhere and on any device.
Payment service providers are under pressure to deliver an engaging and frictionless payment flow across these new customer touchpoints.
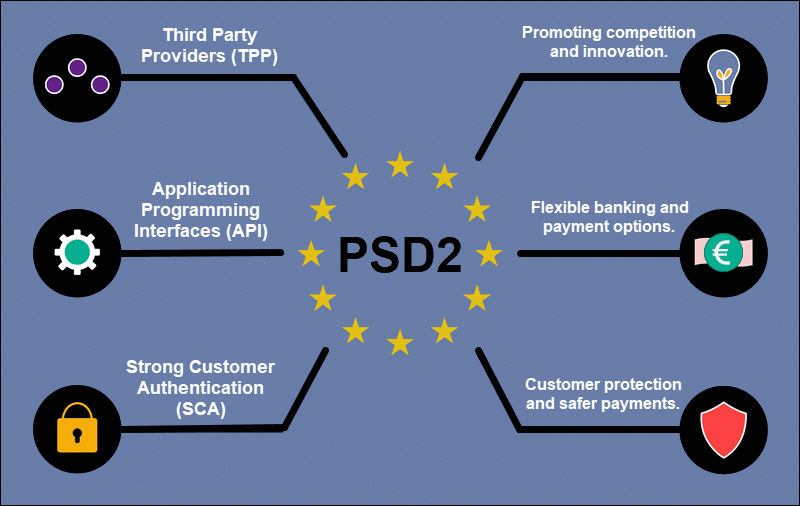
PDS2 is a piece of legislation designed to intensify competition and protect customers and businesses in this fast-paced and fragmented market.
Find out how PSD2 affects your business and use CCBill's SCA-ready solutions to stay ahead of the game.

What is PSD2?
The Revised Payment Services Directive (PSD2) is a legal act that regulates electronic payments within the European Economic Area (EEA).
The directive outlines the rights and responsibilities of customers and payment services providers.
It aims to give customers more control over their data, encourage innovation in the payments industry, and reduce fraudulent activity.
PSD2 establishes rules regarding:
- Payment Authentication - Strong customer authentication (SCA) is now mandatory for most electronic payments in the European Economic Area. By enforcing SCA, regulators hope to prevent fraud, preserve customer data integrity, and mitigate potential disputes.
- Third-Party Providers - Banks and other financial institutions are required to grant third-party providers (TPP) access to their APIs and customers' financial data. Competing TPPs are expected to spearhead innovation and build an entirely new ecosystem around existing financial services.
- Customer Rights - Customers are free to choose between TPPs and decide which providers can access their financial data and for what purposes that data is used. The freedom of choice and added transparency is an opportunity to empower customers and give them more say about how their information is being utilized.
Strong Customer Authentication (SCA) is one of the core requirements of PSD2.
What Is SCA?
SCA is a set of rules that card issuers (banks or other financial institutions) need to adhere to when approving a card-not-present transaction.
Payment service providers need to verify the customer's identity using multi-factor authentication to ensure that online payments cannot be initiated without the payer's knowledge.
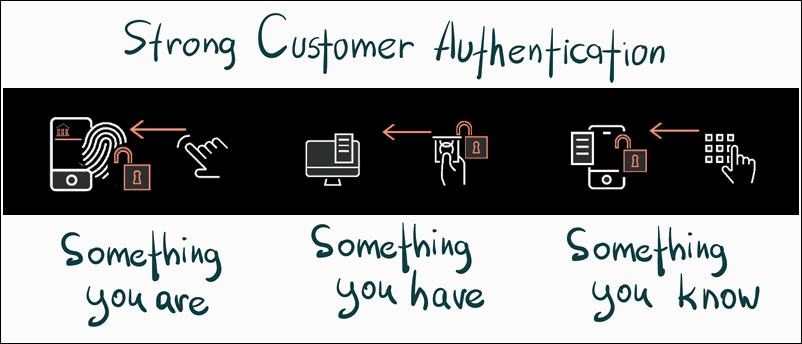
Customers are asked to provide at least two independent pieces of information to prove their identity when paying online.
Each piece of information needs to be obtained from one of the following categories:
- Knowledge - Information only the individual making the payment knows, for example, a PIN or password.
- Possession - An object the customer owns and has access to. The item is usually used to initiate the purchase, such as a debit/credit card, USB token, smartphone, etc.
- Inherence - A trait unique to an individual, including advanced biometric solutions like fingerprint and retinal scans, voice recognition, etc.
To support SCA, merchants and payment processors have to capture and deliver customer data to the card issuer. They need to integrate multi-factor authentication into the payment flow.
The payment flow and authentication process must be secure, straightforward, and must not disrupt the customer's experience.
3DS is one of the most widely used security protocols for strong customer authentication.
How Does PSD2 Impact Your Business?
The card issuer (customer's bank) is responsible for approving or denying the transaction based on SCA results.
Since the scope of PSD2 is limited to the European Economic Area:
- Customers paying on a European merchant's website with a card issued by a European bank should always be authenticated using SCA. Only certain types of transactions, such as corporate wires, small-amount payments, recurring transactions, etc., are exempt from authentication.
- European customers paying on non-European websites may be subject to SCA if the acquirer (merchant's bank) supports SCA.
- Customers from non-European countries, for example, US customers, are not subject to a mandatory SCA check even if they are traveling in the EU or paying on European websites.
- Non-European banks are not required to use strong customer authentication unless mandated by local regulations. However, some banks have decided to implement SCA to verify high-value transactions or other payments they consider to be high-risk.
The decision to implement an SCA solution depends on where your business is registered and if you sell products and services in the European market:
- European merchants that accept payments from European customers need to implement an SCA solution.
- Non-European merchants, for example, US merchants who want to accept payments from European customers are not required to adopt SCA, but it is highly recommended they do so.
- Non-European merchants that do not accept payments from European customers do not need to implement SCA unless required by local laws.
SCA has several clear benefits:
- Liability Shift - If the card issuer approves an SCA transaction, they usually accept liability in case of a dispute, such as a fraud-related chargeback request.
- Security - Strong authentication has been around for many years. The technology is tried and tested. Customers in Europe are already accustomed to SCA and appreciate the added security layer.
- Implementation - Established payment processors, like CCBill, offer SCA-ready solutions that are easy to set up and require minimal updates to the merchant's apps and systems.
SCA has also received its share of criticism:
- Higher Abandonment Rates - The additional authentication step has increased cart abandonment rates. Merchants feel that SCA requirements are going to lead to lower revenue, regardless of how well the payment flow is designed.
- Too Many Moving Parts - The many participants in an SCA payment process make it difficult to maintain full system readiness 24/7. A technical issue at any stage of the authentication process is a potential bottleneck. For example, if a customer's mobile carrier cannot deliver an OTP in the required timeframe, the customer cannot complete their purchase.
CCBill's payment APIs and SCA-ready solutions are designed to help you adjust your payment flows and meet PSD2 requirements.
CCBill SCA-Ready Solution
Merchants know how much time and effort it takes to set up a seamless payment flow that perfectly fits their business model.
CCBill's solutions allow merchants to easily update the payment flows on their websites and apps to support strong customer authentication.
CCBill has implemented the 3DS protocol across its payment systems and is fully compliant with PSD2 regulations. When strong authentication is required, CCBill authenticates the customer using an OTP (one-time-password), PIN, or biometric data, depending on what the customer's bank supports.
FlexForms
The FlexForms system is CCBill's user-friendly environment for designing and building payment forms and flows.
The payment forms are fully responsive and recognize devices, browsers, and the customer's location to display the optimal payment options.
FlexForms support 3DS authentication by default. Merchants can implement SCA simply by placing a payment form link on their website. No additional setup is necessary.
The link to the payment form only needs to be placed once. Merchants do not need to change payment links when modifying a form or flow.
Customers are automatically assessed based on the information they enter on the payment form. If the customer is required to pass a strong authentication process, they are prompted to authorize the payment by providing an additional authentication factor, like an OTP.
Use Case: Recurring Monthly Subscription
1. Customers initiate an online payment from a payment form and enter their card information, including the CVV (possession).
2. If the transaction requires an SCA, the customer is presented with a screen to enter an OTP (knowledge) and confirm that they initiated the transaction.
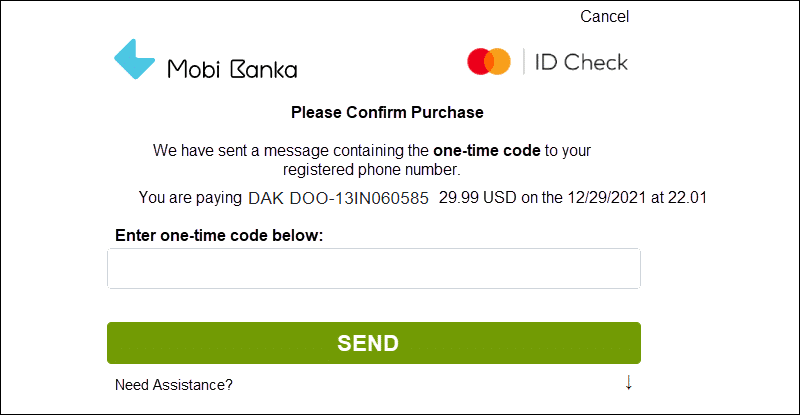
3. The OTP is typically delivered to the customer's phone using an SMS or push notification. The phone number is registered with the customer's bank.
4. If the code is correct, the card issuer (customer's bank) approves the transaction.
The customer is granted access to the paid content.
Subsequent recurring monthly charges do not require additional 3DS authentication.
PSD2 Going Forward
Since PSD2 has been in effect in the EU it has reduced fraud and expanded customer rights.
Important anti-fraud measures PSD2 introduced include:
- Payment services providers are required to develop clear dispute-resolving procedures, comply with PSD2, and ensure fast responses to customer payment complaints (within 15 business days as opposed to the previous 8-week regulatory requirement).
- Payments made in non-EU currencies and transactions in which one of the payment service providers is a non-EU resident are now regulated by PSD2.
- The regulation provides a legal framework for an unconditional ("no questions asked") refund right for direct debit in euros.
- The amount a customer cannot recover from their payment provider or bank when an unauthorized payment occurs has been lowered from €150 to €50. This does not apply in cases of the customer's gross negligence or fraud.
- In preauthorized card transactions with an unspecified final amount, the recipient can reserve the funds from the payer's account only once the card owner has entered and approved the total amount.
While PSD2 unquestionably improves online security, it also leads to payment friction. Merchants are seeing a significant increase in cart abandonment rates. Payment service providers and TPPs are scrambling to develop new multi-factor authentication tools and streamline the payment process.
The European Banking Authority has anticipated this issue and exempts certain transactions from mandatory SCA. These include:
- Recurring transactions and subscriptions - Recurring customers making regular fixed-amount payments to subscription businesses won't have to undergo SCA every time they make the payment, only during the initial payment.
- Safelisting trusted sources - Customers can safelist merchants they trust so that SCA doesn't apply. Consumers usually safelist merchants they buy from often.
- Contactless payments below €50 - PSD2 doesn't require SCA for contactless payments below €50. However, SCA applies if a customer makes four or more €50-payments in succession and surpasses the €150 threshold.
- Transactions below €30 - Every card-not-present transaction below €30 is exempted from SCA. However, SCA is required in the case of four or more €30-payments in succession, which cross the €100 threshold.
- Low-risk payments - SCA is not mandatory if the acquirer's fraud rate is lower than 0.13%, 0.06%, and 0.01% for payments up to €100, €250, and €500, respectively.
- One owner, more accounts - If a person transfers funds from one account they own to another, no SCA is necessary.
Before PSD2 was introduced, only banks were permitted to handle payment account data.
Allowing AISPs (account information service providers) and PISPs (payment initiation service providers) to access customer financial data is going to open up markets to new players and lead to more competition.
Merchants will benefit from this process by gaining access to valuable aggregated data that was previously unavailable.
Conclusion
PSD2 is going to shape the electronic payments market in the EU for years to come. It will precipitate new banking and payment services and decentralize the payments industry.
There is no doubt that customers in the European market will be the main benefactors from this rapid diversification of services.
